| C H A P T E R 4 |
|
Connecting the Data Cables |
This chapter provides the data cabling instructions for the Netra 240 server, and contains the following sections:
|
Note - See Chapter 5 for a listing of the power site requirements and the instructions for assembling and connecting the power cables. |
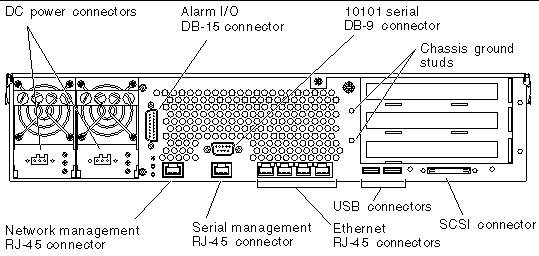
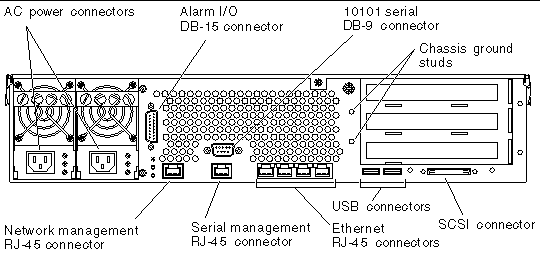
FIGURE 4-1 displays the location of the rear cable connectors of the DC server, FIGURE 4-2 displays the AC server's rear cable connectors, and TABLE 4-1 describes these connectors.
|
DC power input cables connect to each DC connector. Do not connect the power cables to a DC connector at this point. Note: See Chapter 5 for instructions on assembling and connecting the DC power cables. |
||
|
AC power input cables connect to each AC connector. Do not connect the power cables to a AC connector at this point. Note: See Chapter 5 for instructions on assembling and connecting the AC power cables. |
||
|
In a telecommunications environment, use this port to connect to the central office alarming system. |
||
|
Use these studs to connect the server to protected earth ground. |
||
|
Use this port for making an Ethernet connection to the ALOM software. |
||
|
Use this serial port for server management using the ALOM software. |
||
|
Use these ports to connect to autonegotiating 10/100/1000BASE-T Ethernet networks. |
||
Before installing any other cable, you should first attach the chassis ground cable to the server's chassis grounding studs. Refer to the Chapter 5 for the site requirements for this section.
1. Obtain a chassis grounding cable from your site and two M5 nuts with lock washers from the ship kit.
2. Go to the back of the server and locate the two chassis grounding studs (see FIGURE 4-3).
3. Position and align the chassis grounding cable against the two grounding studs at the rear of the chassis.
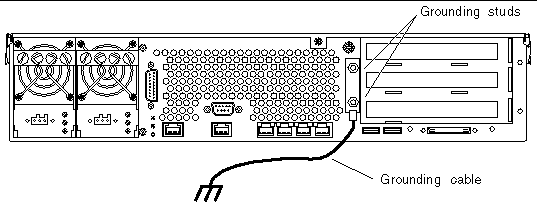
4. Tighten the two M5 nuts to secure the grounding cable to the two studs.
5. Secure the other end of the grounding cable to the earth ground in the building.
You can secure the grounding cable to a proper grounding point on the rack, as long as the rack is properly grounded to the earth ground in the building.
|
Caution - An electrical hazard is present if energized units are not properly grounded. |
This section provides information about the rear panel cable connections.
|
Note - See Chapter 5 for complete information about assembling and connecting the power cables. |
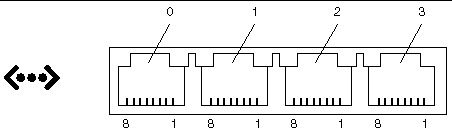
The Netra 240 server has four autonegotiating 10/100/1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet system domain ports. All four Ethernet ports use a standard RJ-45 connector, the transfer rates for which are given in TABLE 4-2. FIGURE 4-4 shows the pin numbering of the ports, and TABLE 4-3 describes the pin signals.
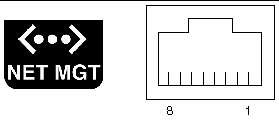
The server has one 10BASE-T Ethernet management domain interface, labelled NET MGT. For information on configuring this port for managing the server with ALOM, see the Sun Advanced Lights Out Manager User Guide for the Netra 240 Server
(817-3174).
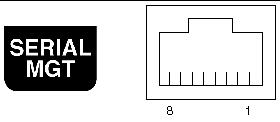
The server has two serial ports, labeled SERIAL MGT and 10101. TABLE 4-5 lists the default serial connection settings for both serial ports.
The serial management connector (labeled SERIAL MGT) is an RJ-45 connector that can be accessed from the back panel. This port is the default connection to the system, and you should use this port only for server management.
|
Caution - You must use a shielded Ethernet cable to maintain your server's NEBS compliance. The cable's shield must be grounded at both ends. |
FIGURE 4-6 shows the pin numbering of the serial management port, and TABLE 4-6 describes the pin signals.
If you need to connect to the SERIAL MGT port using a cable with either a DB-9 or a DB-25 connector, use a supplied adapter to perform the crossovers given for each connector. The supplied RJ-45 to DB-9 and RJ-45 to DB-25 adapters are wired as described in TABLE 4-7 and TABLE 4-8.
The port labeled 10101 accepts a DB-9 connector. Use this port for general purpose serial data transfers. FIGURE 4-7 shows the pin numbering of the serial port, and TABLE 4-9 describes the pin signals.
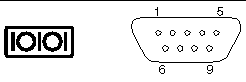
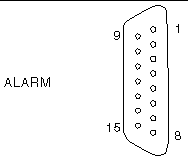
The alarm port on the alarm rear transition card uses a standard DB-15 male connector. In a telecommunications environment, use this port to connect to the central office alarming system. FIGURE 4-8 shows the pin numbering of the alarm port, and TABLE 4-10 describes the pin signals.
|
ALARM0_NC[1] |
|||
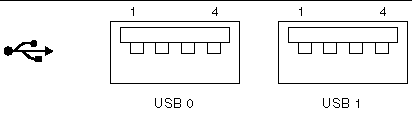
The server has two USB ports for attaching supported USB 1.1-compliant devices. FIGURE 4-9 shows the pin numbering of the USB ports, and TABLE 4-11 describes the pin signals.
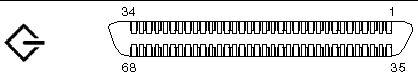
The SCSI port is a multimode Ultra 160SCSI interface. To operate at Ultra 160SCSI speeds, the part must be in Low-Voltage Differential (LVD) mode. If a single-ended device is connected to the server, it automatically switches to single-ended mode. FIGURE 4-10 shows the pin numbering of the SCSI port, and TABLE 4-12 describes the pin signals.
 When the system is in Standby mode.
When the system is in Standby mode.
 When the server is powered on and the operating system has not booted or has failed.
When the server is powered on and the operating system has not booted or has failed.
Copyright © 2004, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.