|
|
< Previous | Next > |
| Product: Volume Manager Guides | |
| Manual: Volume Manager 4.1 Administrator's Guide | |
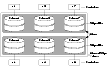
Creating a Volume on Specific DisksVxVM automatically selects the disks on which each volume resides, unless you specify otherwise. If you want a volume to be created on specific disks, you must designate those disks to VxVM. More than one disk can be specified. To create a volume on a specific disk or disks, use the following command: # vxassist [-b] [-g diskgroup] make volume length [layout=layout] \ diskname ... For example, to create the volume volspec with length 5 gigabytes on disks mydg03 and mydg04, use the following command: # vxassist -b -g mydg make volspec 5g mydg03 mydg04 The vxassist command allows you to specify storage attributes. These give you control over the devices, including disks, controllers and targets, which vxassist uses to configure a volume. For example, you can specifically exclude disk mydg05: # vxassist -b -g mydg make volspec 5g !mydg05 or exclude all disks that are on controller c2: # vxassist -b -g mydg make volspec 5g !ctlr:c2 or include only disks on controller c1 except for target t5: # vxassist -b -g mydg make volspec 5g ctlr:c1 !target:c1t5 If you want a volume to be created using only disks from a specific disk group, use the -g option to vxassist, for example: # vxassist -g bigone -b make volmega 20g bigone10 bigone11 or alternatively, use the diskgroup attribute: # vxassist -b make volmega 20g diskgroup=bigone bigone10 bigone11 You can also use storage attributes to control how vxassist uses available storage, for example, when calculating the maximum size of a volume, when growing a volume or when removing mirrors or logs from a volume. The following example excludes disks dgrp07 and dgrp08 when calculating the maximum size of RAID-5 volume that vxassist can create using the disks in the disk group dg: # vxassist -b -g dgrp maxsize layout=raid5 nlog=2 !dgrp07 !dgrp08 See the vxassist(1M) manual page for more information about using storage attributes. It is also possible to control how volumes are laid out on the specified storage as described in the next section Specifying Ordered Allocation of Storage to Volumes. Specifying Ordered Allocation of Storage to VolumesOrdered allocation gives you complete control of space allocation. It requires that the number of disks that you specify to the vxassist command must match the number of disks that are required to create a volume. The order in which you specify the disks to vxassist is also significant. If you specify the -o ordered option to vxassist when creating a volume, any storage that you also specify is allocated in the following order: For example, the following command creates a mirrored-stripe volume with 3 columns and 2 mirrors on 6 disks in the disk group, mydg: # vxassist -b -g mydg -o ordered make mirstrvol 10g \ layout=mirror-stripe ncol=3 \ mydg01 mydg02 mydg03 mydg04 mydg05 mydg06 This command places columns 1, 2 and 3 of the first mirror on disks mydg01, mydg02 and mydg03 respectively, and columns 1, 2 and 3 of the second mirror on disks mydg04, mydg05 and mydg06 respectively. This arrangement is illustrated in Example of Using Ordered Allocation to Create a Mirrored-Stripe Volume. Example of Using Ordered Allocation to Create a Mirrored-Stripe Volume Click the thumbnail above to view full-sized image. For layered volumes, vxassist applies the same rules to allocate storage as for non-layered volumes. For example, the following command creates a striped-mirror volume with 2 columns: # vxassist -b -g mydg -o ordered make strmirvol 10g \ layout=stripe-mirror ncol=2 mydg01 mydg02 mydg03 mydg04 This command mirrors column 1 across disks mydg01 and mydg03, and column 2 across disks mydg02 and mydg04, as illustrated in Example of Using Ordered Allocation to Create a Striped-Mirror Volume. Example of Using Ordered Allocation to Create a Striped-Mirror Volume Click the thumbnail above to view full-sized image. Additionally, you can use the col_switch attribute to specify how to concatenate space on the disks into columns. For example, the following command creates a mirrored-stripe volume with 2 columns: # vxassist -b -g mydg -o ordered make strmir2vol 10g \ layout=mirror-stripe ncol=2 col_switch=3g,2g \ mydg01 mydg02 mydg03 mydg04 mydg05 mydg06 mydg07 mydg08 This command allocates 3 gigabytes from mydg01 and 2 gigabytes from mydg02 to column 1, and 3 gigabytes from mydg03 and 2 gigabytes from mydg04 to column 2. The mirrors of these columns are then similarly formed from disks mydg05 through mydg08. This arrangement is illustrated in Example of Using Concatenated Disk Space to Create a Mirrored-Stripe Volume. Example of Using Concatenated Disk Space to Create a Mirrored-Stripe Volume Click the thumbnail above to view full-sized image. Other storage specification classes for controllers, enclosures, targets and trays can be used with ordered allocation. For example, the following command creates a 3-column mirrored-stripe volume between specified controllers: # vxassist -b -g mydg -o ordered make mirstr2vol 80g \ layout=mirror-stripe ncol=3 \ ctlr:c1 ctlr:c2 ctlr:c3 ctlr:c4 ctlr:c5 ctlr:c6 This command allocates space for column 1 from disks on controllers c1, for column 2 from disks on controller c2, and so on as illustrated in Example of Storage Allocation Used to Create a Mirrored-Stripe Volume Across Controllers. Example of Storage Allocation Used to Create a Mirrored-Stripe Volume Across Controllers Click the thumbnail above to view full-sized image. For other ways in which you can control how vxassist lays out mirrored volumes across controllers, see Mirroring across Targets, Controllers or Enclosures. |
| ^ Return to Top | < Previous | Next > |
| Product: Volume Manager Guides | |
| Manual: Volume Manager 4.1 Administrator's Guide | |
|
VERITAS Software Corporation
www.veritas.com |