Serial Ports Test (sptest)
|
sptest checks the system's on-board serial ports (zs[0,1], zsh[0,1], se[0,1], se_hdlc[0,1]), as well as any multi-terminal interface (ALM2) boards (mcp[0-3]). Data is written and read in asynchronous and synchronous modes utilizing various loopback paths.
Intervention mode must be enabled to run this test.
This test is nonscalable.
sptest dynamically probes for se, zs, zsh, and se_hdlc ports for testing. All error messages, warning messages, and options in the test parameter options dialog box are set dynamically to the correct port names. For example, if a system's a and b ports are su ports, and c and d are se ports, sptest will test ports c and d. The test parameter dialog box will also show the correct ports in its menu options, such as "Test Type: c to d," etc. See FIGURE 53-1 for an example of the test parameter dialog box.
TABLE 53-1 Serial Port Tests
|
Mode
|
Description
|
|
Asynchronous testing
|
This mode uses the asynchronous communication protocol as described in the zs(7D)and se(7D)man pages. The termio(7I)interface is used for configuring port characteristics.
The user can select the loopback paths to use, the amount of data to transfer, and the baud rate to use.
The test writes and reads data through the loopback path and compares the data to the original data. The test first sends a single character. If no errors or timeouts are detected, the rest of the data is simultaneously written and read, then compared.
|
|
Synchronous testing
|
This mode uses the synchronous hdlc-framing interface as described in the zsh(7D) and se_hdlc(7D) man pages. Data is written and read in checksum-protected packets.
The user can select the loopback paths to use and the clock rate.
The synchronous test runs in three phases:
-
The first phase looks for activity on the port. If no activity is detected for at least four seconds, the test proceeds to the next phase. If activity is detected sptest exits with an error.
-
The second phase attempts to send and receive one packet. If no packets are detected after five attempts, the test exits with an error. If a packet is returned, the result is compared to the original. If the length and content of the packets do not match exactly, the test exits with an error.
-
The third phase attempts to send many packets through the loop. Some packet drops are to be expected especially on a heavily loaded system. The test allows a percentage of the packets to be dropped. The user can set the drop tolerance between 0 percent and 99 percent. The default is 20 percent. If the system is extremely busy then the drop tolerance should be increased. Each packet is compared with its original for length and content. If a mismatch is detected, the test exits with an error.
|
sptest Synchronous Testing Software Requirements
If you have zs(7D) serial ports on your machine, the synchronous devices may not exist. Look in the /dev directory for zsh (where h=0 and/or 1). If they do not exist, you can create them.
|
 To Create Synchronous Devices To Create Synchronous Devices
|
1. Verify that the following two lines are in the /etc/devlink.tab file. If they are not there, add them.
type=ddi_pseudo;name=zsh zsh\M0
type=ddi_pseudo;name=clone;minor=zsh zsh
|

|
Caution - The white spaces in the lines above must be a single tab character before and after the zsh variables; using spaces will not work.
|
2. When the lines have been added to the /etc/devlink.tab file, change directories to /kernel/drv and run the add_drv zsh command.
3. If this command does not work, run the rem_drv zsh command and then run the add_drv zsh command again.
sptest Options
To reach the dialog box below, right-click on the test name in the System Map and select Test Parameter Options. If you do not see this test in the System Map, you might need to expand the collapsed groups, or your system may not include the device appropriate to this test. Refer to the SunVTS User's Guide for more details.
FIGURE 53-1 sptest Test Parameter Options Dialog Box
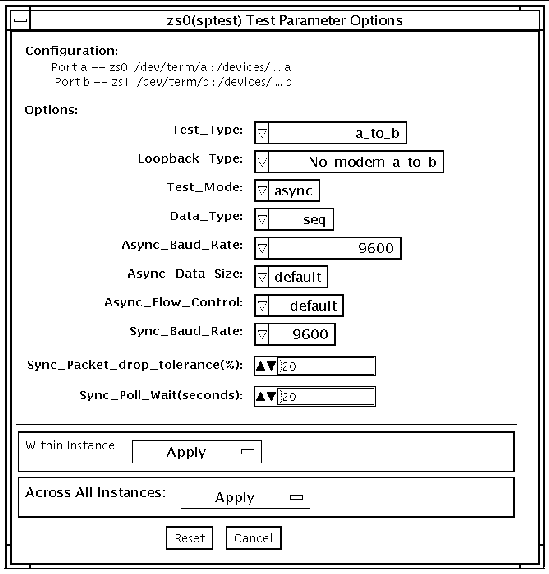
There are a variety of loopback paths available. The internal loopback paths do not require an external connector. Their availability depends on the device. The zs(7D) device has an internal path for synchronous mode and the se(7D) device has an internal path for asynchronous mode. The external loopback connectors are described in Appendix A. The exact type of loopback connector required depends on the system I/O panel.
Some examples of loopback test commands follow. For a full description of command-line syntax, see sptest Command-Line Syntax.
To test /dev/term/b from the command line using internal loopback, type the following:
% ./sptest -vf -o M=async,T=b,L=I
|
To test /dev/term/b from the command line using external loopback, type:
% ./sptest -vf -o M=async,T=b,L=P
|
For zs(7D) machines, the internal loopback path is only active in synchronous mode:
% ./sptest -vf -o M=sync,T=b,L=I
|
The following table lists the possible devices for each port. Below, "a" represents port a of the CPU board (motherboard), "b" represents port b of the CPU board, and the device names of the ports for each CPU board are listed.
TABLE 53-2 sptest Serial Devices
|
CPU
|
Port
|
Async Device
|
Sync Device
|
|
0
|
a
b
|
zs0 or se0
zs1 or se1
|
zsh0 or se_hdlc0
zsh1 or se_hdlc1
|
|
1
|
a
b
|
zs2
zs3
|
zsh2 *
zsh3 *
|
|
2
|
a
b
|
zs4
zs5
|
zsh4 *
zsh5 *
|
|
* Currently, only zsh0 and zsh1 are supported by device drivers.
|
TABLE 53-3 sptest Options
|
sptest Options
|
Description
|
|
Test Type
|
Selects how the test will run. Test options include:
 a= runs the test on port a a= runs the test on port a
 b= runs the test on port b b= runs the test on port b
 a_b= runs the test on ports a and b sequentially a_b= runs the test on ports a and b sequentially
 a_b_concurrent= runs the test on port a and port b concurrently. a_b_concurrent= runs the test on port a and port b concurrently.
|
|
Loopback Type
|
Selects the loopback test. Options include:
 Internal is an internal path for a, b, a_b, and a_b_concurrent test types. Internal is an internal path for a, b, a_b, and a_b_concurrent test types.
 Plug_a_to_a__b_to_b is an external loopback plug for a, b, a_b, and a_b_concurrent test types. Plug_a_to_a__b_to_b is an external loopback plug for a, b, a_b, and a_b_concurrent test types.
 no_modem_a_to_b is an external loopback cable for a_to_b and a_to_b_concurrent test types. no_modem_a_to_b is an external loopback cable for a_to_b and a_to_b_concurrent test types.
 Modem_a_to_b is an external loopback cable with a modem attached to generate synchronous Transmit and Receive clocks in synchronous mode. The modem a_to_b external loopback type is intended for Sun internal use only. It requires custom equipment that is not available. Modem_a_to_b is an external loopback cable with a modem attached to generate synchronous Transmit and Receive clocks in synchronous mode. The modem a_to_b external loopback type is intended for Sun internal use only. It requires custom equipment that is not available.
|
|
Test Mode
|
Selects the mode to put the serial device into before running the test. The modes available are Asynchronous, Synchronous or Both. When Both is selected, the test runs in Asynchronous mode then Synchronous mode.
|
|
Data Type
|
Selects the data pattern to transfer. The user can select:
 Random Random
 Sequential Sequential
 Alphanumeric Alphanumeric
 0x00-0xff 0x00-0xff
|
|
Async Baud Rate
|
Selects the baud rate for Asynchronous mode testing. The valid rates are: 110, 300, 600, 1200, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 76800, 115200, 153600, 230400, 307200, 460800, and ALL. The default rate is 9600 baud. Some platforms can only support up to 38400 or 76800. The test will return an error if you try to use a higher baud rate then is supported. For baud rates greater then 153600 the serial line drivers must be set for RS-423 mode and not RS-232 mode. The RS-423 and RS-232 modes are usually selected by a hardware jumper on the motherboard. Consult your hardware installation manual for more information.
|
|
Async Data Size
|
Selects the total number of bytes to transfer in Asynchronous mode. This can range from 1 to 10000.
|
|
Async Flow Control
|
Selects the type of flow control to use in asynchronous mode testing. The user can select Hardware (RTS/CTS), Software (XON/XOFF) or None. The default depends on the loopback type. Software flow control is not allowed on a, b, a_b, or a_b_concurrent loopback types.
|
|
Sync Baud Rate
|
Selects the device generated clock rate for synchronous mode testing. The valid rates are from 110 to 230400. The rate does not have to be a specific value as required for async mode baud rates. The default rate is 9600. Some platforms can only support up to 38400 or 76800. The test will return an error if you try to use a higher rate then is supported. For rates greater then 100000 the serial line drivers must be set for RS-423 mode and not RS-232 mode. The RS-423 and RS-232 modes are usually selected by a hardware jumper on the motherboard. Consult your hardware installation manual for more information.
|
|
Sync Packet Drop Tolerance
|
Selects the tolerance level of Synchronous mode dropped packets during the many_packets subtest. The default is 20 percent. The valid range is from 0 percent to 99 percent. Some packet drops are expected especially at higher clock rates and on a heavily loaded system.
|
|
Sync Poll Wait
|
Selects the number of seconds in additional time to wait for a Synchronous mode packet to be sent. Additional time may be needed when there is heavy system activity and time-outs are being detected. In general, the user can decrease the value to 0 when the system load is light or increase the value when there is a heavy system load.
|
sptest Test Modes
sptest supports the following SunVTS test modes.
TABLE 53-4 sptest Supported Test Modes
|
Test Mode
|
Description
|
|
Connection
|
Attempts to open the port to determine if the device is connected. If it fails and the port is not busy, the test exits with an error. If it is successful or fails with a busy or exclusive use error, then the port is considered connected, and the test passes.
|
|
Functional
(Offline)
|
Performs the selected loopback test.
|
|
Online
|
Performs the full set of tests.
|
sptest Command-Line Syntax
/opt/SUNWvts/bin/sptest standard_arguments -o dev=device_name, porta=port_name,T=test_type,L=loopback_type,M=mode,D=data_pattern, AB=async_baud_rate,S=async_data_size,par=none|even|odd,BS=1|10|100|1000 |3000|5000|10000,F=flow_control,B=sync_baud_rate,DP=sync_drop_tolerance, P=sync_poll_wait
TABLE 53-5 sptest Command-Line Syntax
|
Argument
|
Description
|
|
dev=device_name
|
Identifies the serial port(s) to test. There is no default value. You must specify a device name such as:
-
se0,
-
zs0, zs1
-
zs2, zs3
-
..., ...
|
|
porta=port_name
|
The name of the first device of a serial device pair. The default is a.
|
|
T=test_type
|
Specifies the type of test to run:
-
a= runs the test on port a.
-
b= runs the test on port b.
-
a_b= runs the test on ports a and b sequentially.
-
a_b_concurrent= runs the test on port a and port b concurrently.
-
a_to_b= runs the test from port a to port b.
|
|
L=loopback_type
|
The type of loopback connector attached to ports:
-
No_modem_a_to_b
-
Internal_a_to_a__b_to_b
-
Plug_a_to_a__b_to_b
-
Modem_a_to_b
|
|
M=mode
|
The default test mode is asynchronous. Specify one of the following modes:
|
|
D=data_pattern
|
Selects the data pattern to transfer. The user can select:
-
Random
-
Sequential
-
Alphanumeric
-
0x00-0xFF
|
|
AB=async_baud_rate
|
Asynchronous baud rate (default = 9600). The valid values are between 110 - 460800.
Note: Some platforms can only support asynchronous baud rates up to 38400 or 76800. For baud rates greater then 153600 the serial line drivers must be set for RS-423 mode and not RS-232 mode.
|
|
S=async_data_size
|
Asynchronous mode total number of bytes to write; from 1 to 10000 bytes.
|
|
par=none|even|odd
|
Parity used in the async loop test. Default value is none.
|
|
BS=1|10|100|1000| 3000| 5000|10000
|
Number of bytes in each write during async loop test. Default value is 100.
|
|
F=flow_control
|
Asynchronous mode flow control:
-
Hardware (RTS/CTS)
-
Software (xon/xoff)
-
None
|
|
B=sync_baud_rate
|
Synchronous baud rate (default = 9600). The valid rates are between 110 - 256000.
Note: Some platforms can only support synchronous rates up to 38400 or 76800. For rates greater then 100000 the serial line drivers must be set for RS-423 mode and not RS-232 mode.
|
|
DP=sync_drop_tolerance
|
Synchronous mode drop packet tolerance (default=20 percent).
|
|
P=sync_poll_waitt
|
Synchronous mode additional wait time during poll (in seconds).
|
|
Note - 64-bit tests are located in the sparcv9 subdirectory: /opt/SUNWvts/bin/sparcv9/testname. If a test is not present in this directory, then it may only be available as a 32-bit test. For more information refer to 32-Bit and 64-Bit Tests.
|
| SunVTS 5.1 Test Reference Manual
| 816-5145-10
|    
|
Copyright © 2002, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.

