| C H A P T E R 2 |
|
Cluster Platform 220/1000 |
Cluster Platform 220/1000 provides self-sustained platforms, integrated through the Sun Cluster technology, to support highly available applications. This two-node cluster system with shared access to 200 Gbytes of mirrored Ultra-SCSI storage can be used to implement a highly available file server, web server, or mail server.
Sun Cluster technology provides global file systems, global devices, and scalable services. These features allow independent cluster nodes, running independent Solaris Operating Environment instances, to run distributed applications while providing client access through a single IP address.
Your system contains the standard Sun hardware and software required for a cluster environment. This integrated system significantly reduces the complexity and implementation time associated with a cluster setup. The hardware and software are integrated by Sun, using established best practices extracted from engineering recommendations or through field experience, to help increase system availability.
|
Note - This Cluster configuration only provides a basic cluster environment. Data services must be installed and configured by the customer. |
Your system includes a two-node cluster with shared, mirrored storage, a terminal concentrator, and a management server. The hardware components are installed in the rack in compliance with existing power, cooling, and electromagnetic interference (EMI) requirements. These components are cabled to provide redundant cluster interconnect between nodes, and to provide access to shared storage and production networks.
The management server is the repository for software and patches that are loaded on the system. The management server provides access to the cluster console, and it functions as a JumpStart server (install server) for the cluster nodes.
server (install server) for the cluster nodes.
|
Note - The management server has sufficient CPU power and memory to implement a Sun |
To integrate your Cluster Platform 220/1000 into a production environment, you must:
1. Remove the lower front panel of the rack.
2. Connect the power cord to the front and rear sequencer, and power on both breaker switches. Replace the front panel.
3. Provide a name, IP address and root password for the management server.
4. Provide a name and IP address for the terminal concentrator.
5. Provide a name for the cluster environment and a default router (gateway).
6. Provide names and IP addresses for individual cluster nodes.
7. Configure shared disk storage under Solstice DiskSuite or VERITAS volume manager. Configuration includes the creation of disksets (or disk groups), disk volumes, and file systems.
8. Select a quorum device from the shared disk storage.
9. Install and configure the required highly available applications.
10. Install and configure data services to support the highly available applications.
11. Configure Network Adapter Failover (NAFO) for automatic failover.
|
Note - This document does not provide information to support items 7 through 11. For specific implementation details, refer to the Sun Cluster 3.0 documentation. |
The Ethernet address for each cluster node is located on the Customer Information, System Record sheet. Use the serial number on the information sheet and on the back of each node to correctly identify the Ethernet address. (See See Sun Cluster Standard Rack Placement for the placement of each cluster node.)
TABLE 2-1 provides a worksheet to assist with networking information. You will be referred back to the information you place in this table when you customize the cluster configuration.
The Cluster Platform 220/1000 software packages include the following:
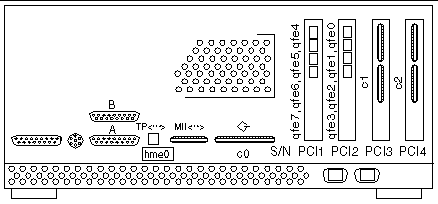
FIGURE 2-2 shows cluster node interface qfe0 providing network automatic failover (NAFO) for hme0 (production network). Interfaces qfe1 and qfe5 are used for the cluster interconnect. Interfaces qfe2, qfe3, qfe4, and qfe7 are available to expand application network services.
|
Note - See Ethernet IP Address Worksheet to specify the appropriate information for your network environment. |
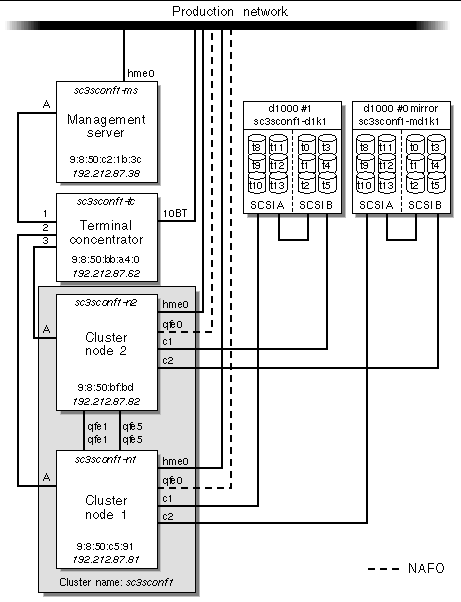
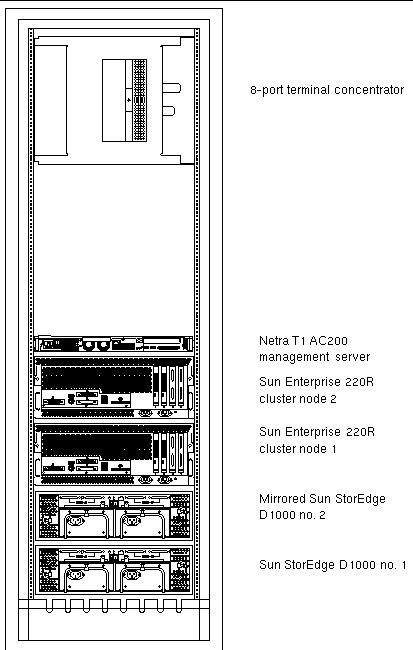
FIGURE 2-3 shows how all of the Cluster Platform 220/1000 are arranged in the expansion cabinet. TABLE 2-2 lists the rack components and the quantities required.
|
Note - The rack arrangement complies with weight distribution, cooling, EMI, and power requirements. |
The Cluster Platform 220/1000 hardware should have two dedicated AC breaker panels. The cabinet should not share these breaker panels with other, unrelated equipment. The system requires two L30-R receptacles for the cabinet, split between two isolated circuits. For international installations, the system requires two Blue 32AIEC309 (international) receptacles.
If the cabinet is installed on a raised floor, cool conditioned air should be directed to the bottom of each rack through perforated panels.
The 72-inch cabinet in Cluster Platform 220/1000 consumes power and dissipates heat, as shown in TABLE 2-3.
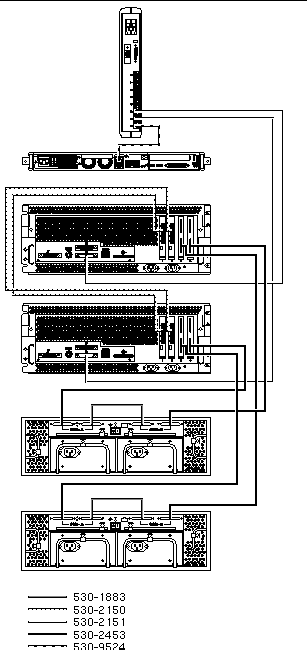
The Cluster Platform 220/1000 is shipped with the servers and each of the arrays already connected in the cabinet. You should not need to cable the system. Refer to TABLE 2-4 for servicing the cables.
This section describes how the Cluster Platform 220/1000 components are cabled when shipped from the factory. The standard configuration provides cables connected to the GBICs on the I/O board.
For specific cabling connections, refer to Appendix C.
When the Cluster Platform 220/1000 is shipped from the factory, the Netra T1 AC200 is preloaded with all of the necessary software to install the cluster nodes with the Solaris operating environment and Sun Cluster 3.0 software.
Because all of the cables are connected and labeled in the factory, configuring the terminal concentrator first will enable the cluster administrator to easily configure the cluster.
|
Note - You must enter the correct parameters for the initial customization, or the configuration will not initialize properly. |
|
Note - To produce a console terminal using a laptop computer, refer to Appendix A. |
1. Power up the main circuit breakers, and then power up all individual system components.
2. Provide console connectivity into the terminal concentrator:
a. Disconnect the serial cable (Part no. 9524A) from Port 1 of the terminal concentrator.
b. Connect the RJ-45 end of the serial cable (Part no. 5121A) to Port 1 of the terminal concentrator and the other end, DB-25 male, to serial port A of a
Sun workstation.
workstation.
|
Note - The tip(1) command connects the Sun workstation I/O with the terminal concentrator I/O during an interactive session. |
c. From a terminal window on the Sun workstation, enter the following command:
# /usr/bin/tip hardwire |
|
Note - If the port is busy, refer to Troubleshooting the Cluster Platform 220/1000 Installation in Appendix D. |
3. Configure the terminal concentrator device:
The terminal concentrator undergoes a series of diagnostics tests that take approximately 60 seconds to complete.
Following the diagnostics tests, the tip window of the administration workstation should display:
System Reset - Entering Monitor Mode monitor:: |
4. Modify the default IP address that will be used in your network. Use the addr command to modify the network configuration of the terminal concentrator. Use the addr -d command to verify the network configuration:
5. Copy the Ethernet address entered above for the terminal concentrator, and add it to Ethernet IP Address Worksheet for later reference when configuring the cluster.
6. Terminate your tip session by entering ~ . (tilde and period). Power-cycle the terminal concentrator to enable the IP address changes and wait at least two minutes for the terminal concentrator to activate its network.
monitor:: ~ . |
a. Disconnect the RJ-45 serial cable (Part no. 5121A) from Port 1 of the terminal concentrator and from the Sun workstation.
b. Reconnect the serial cable (Part no. 9524A) back into Port 1 of the terminal concentrator.
|
Note - At this time, the cluster configuration should be cabled as originally shipped from the factory. |
7. From the Sun workstation, verify that the terminal concentrator responds to the new IP address:
|
Note - The Sun workstation must be connected to the same subnet to which the terminal concentrator was configured. |
8. To access the terminal concentrator, include the default router in the terminal concentrator configuration, and telnet to the terminal concentrator:
|
Note - Change the default terminal concentrator password to avoid unnecessary security exposure. The terminal concentrator password matches the IP address of the terminal concentrator. |
The terminal concentrator opens an editing session and displays an editing config.annex file.
9. Type the following information into the config.annex file; replace the following variable with the IP address obtained from your network administrator.
%gateway net default gateway 192.212.87.248 metric 1 active Ctrl-W: save and exit Ctrl-X: exit Ctrl-F: page down Ctrl-B: page up |
10. Enter the <ctrl>w command to save changes and exit the config.annex file.
11. Enable access to all ports, and reboot the terminal concentrator.
|
Caution - The following steps display critical information for configuring the cluster nodes. Use the Ethernet IP Address Worksheet to collect the Ethernet addresses. Consult your system administrator to obtain the IP addresses and node names for your cluster devices. |
|
Note - Make sure all network interfaces for node 1 and node 2 are attached to the production network. (See See Sun Cluster Standard Interconnections and NAFO for connection details.) |
12. From the Sun workstation, access the terminal concentrator:
# telnet 192.212.87.62 Trying 192.212.87.62... Connected to 192.212.87.62. Escape character is '^]' <CR> Rotaries Defined: cli Enter Annex port name or number: |
a. Enter the command /usr/openwin/bin/xhost 192.212.87.38 to allow your windows manager to display screens from remote systems.
b. Telnet to the telnet concentrator and select Port 1. The following steps will assist you in the configuration of the management server; at the conclusion of the steps, the management server will reboot, and you will be asked a series of questions to configure the cluster.
c. To terminate the telnet session, type <ctrl]>.
13. Boot the management server from the OBP prompt to start the customization process.
The management server boots into the Open Boot Prom (OBP) environment. The following examples show the customization process. The sample parameters may not fit your specific environment. Note the introduction on each code box, and select the best choice for your environment.
|
Caution - Because of the complex nature of this installation, all information and instructions must be followed. If problems arise, a recovery of the management server may be required. |
14. Choose a specific localization.
At this time, only the English and U.S.A. locales are supported. Select a supported locale.
15. Select the appropriate terminal emulation:
After you select the terminal emulation, network connectivity is acknowledged:
The eri0 interface on the management server is intended for connectivity to the production network. You can obtain the management server name, IP address, and root password information from your network administrator:
16. Select Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) services.
Because the management server must have a fixed IP address and name recognized by outside clients, DHCP is not supported:
17. Select the primary network interface.
The management server configuration uses eri0 as the default primary network interface:
18. Enter the name of the management server.
Consult your local network administrator to obtain the appropriate host name. The following management server name is an example.
19. Enter the IP address of the management server.
To specify the management server IP address, obtain it from your local network administrator and enter it at the prompt.
Currently, only version 4 of the IP software is supported. Verify that IPv6 support is disabled.
21. Confirm the customization information for the management server:
22. Deselect and confirm Kerberos security.
Only standard UNIX security is currently supported. Verify that Kerberos security is disabled.
23. Select and confirm a naming service.
Consult your network administrator to specify a naming service. No naming services are selected for the following example.
|
Note - The two cluster nodes will be automatically configured to not support any naming services. This default configuration avoids the need to rely on external services. |
24. Select a subnet membership.
The default standard configuration communicates with network interfaces as part of a subnet.
Consult your network administrator to specify the netmask of your subnet. The following shows an example of a netmask:
26. Select the appropriate time zone and region.
Select the time zone and region to reflect your environment:
27. Set the date and time, and confirm all information.
28. Select a secure root password.
After the system reboots, the cluster environment customization starts. After the system customization is completed, the management server installs the Solstice DiskSuite software and configures itself as an installation server for the cluster nodes.
|
Note - Use "Invalid Cross-Reference Format" on "Invalid Cross-Reference Format" as a reference to input data for Step 29 through Step 33. The variables shown in Step 29 through Step 33 are sample node names and parameters. |
29. After the system reboots, the cluster environment customization starts. After the system customization is completed, the management server completes the Solstice DiskSuite configuration and configure itself as an install server for the cluster nodes.
30. Add the router name and IP address:
Enter the Management Server's Default Router (Gateway) IP Address... 192.145.23.248 |
31. Add the cluster environment name:
Enter the Cluster Environment Name (node names will follow)... sc3sconf1 |
32. Enter the terminal concentrator name (node names will follow):
Enter the Terminal Concentrator Name...sc3conf1-tc Enter the Terminal Concentrator's IP Address...192.145.23.90 |
33. Add the cluster node names and IP addresses:
34. When prompted to confirm the variables, type y if all of the variables are correct. Type n if any of the variables are not correct, and re-enter the correct variables. Enter 99 to quit the update mode, once all variables are displayed correctly.
1. Start cluster console windows for both cluster nodes by entering the following command on the management server:
# /opt/SUNWcluster/bin/ccp sc3sconf1 |
When the /opt/SUNWcluster/bin/ccp command is executed, the Cluster Control Panel window displays (see See Cluster Control Panel Window).
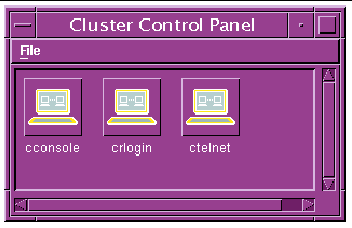
2. In the Cluster Control Panel window, double-click the Cluster Console (console mode) icon to display a Cluster Console window for each cluster node (see FIGURE 2-6).
|
Note - Before you use an editor in a Cluster Console window, verify that the TERM shell environment value is set and exported to a value of vt220. FIGURE 2-7 shows the terminal emulation in the Cluster Console window. |
To issue a Stop-A command to the cluster nodes and to access the OpenBoot PROM (OBP) prompt, position the cursor in the Cluster Console window, and enter the <ctrl>] character sequence. This character forces access to the telnet prompt. Enter the Stop-A command, as follows:
PROM (OBP) prompt, position the cursor in the Cluster Console window, and enter the <ctrl>] character sequence. This character forces access to the telnet prompt. Enter the Stop-A command, as follows:
telnet> send brk ok> |
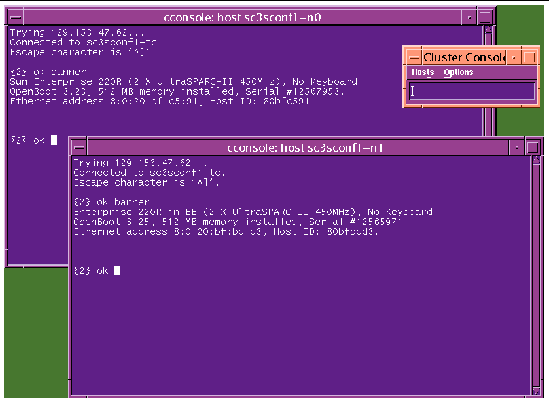
3. To enter text into both node windows simultaneously, click the cursor in the Cluster Console window and enter the text.
The text does not display in the Cluster Console window, and will display in both node windows. For example, the /etc/hosts file can be edited on both cluster nodes simultaneously. This ensures that both nodes maintain identical file modifications.
|
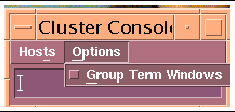
Note - The console windows for both cluster nodes are grouped (the three windows move in unison--FIGURE 2-6). To ungroup the Cluster Console window from the cluster node console windows, select Options from the Hosts menu (FIGURE 2-7) and deselect the Group Term Windows checkbox. |
1. Use the ccp(1M) Cluster Console window to enter the following command into both nodes simultaneously:
{0} ok setenv auto-boot? true {0} ok boot net - install |
|
boot net - You must use spaces between the dash (-) character in the
|
The Solaris operating environment, Solstice DiskSuite, and Sun Cluster 3.0 are automatically installed. All patches are applied and system files are configured to produce a basic cluster environment.
See Appendix B for sample output of the automatic installation of the first cluster node.
|
Note - Disregard error messages received during the initial cluster installation. Do not attempt to reconfigure the nodes. |
2. Log into each cluster node as a superuser (password is abc) and change the default password to a secure password choice:
# passwd passwd: Changing password for root New password: secure-password-choice Re-enter new password: secure-password-choice |
3. Configure the Sun StorEdge D1000 shared disk storage using the Solstice DiskSuite software.
Solstice DiskSuite configuration involves creating disksets, metadevices, and file systems. (Refer to the included Sun Cluster 3.0 documentation.)
4. Select a quorum device to satisfy failure fencing requirements for the cluster. (Refer to the included Sun Cluster 3.0 documentation.)
5. Install and configure the highly available application for the cluster environment. (Refer to the Sun Cluster 3.0 documentation.)
Establish resource groups, logical hosts, and data services to enable the required application under the Sun Cluster 3.0 infrastructure. (Refer to the Sun Cluster 3.0 documentation.)
The path to the data CD is /net/{management server}/SOFTWARE/SC3.0-Build92DataServices
Your customized Cluster Platform 220/1000 is completed.
The recovery CDs enable you to replace the factory-installed Cluster
Platform 220/1000 software environment on the management server in the event of a system disk failure.
|
Caution - Initiate a recovery only at the direction of technical support. |
These CDs are intended only for recovering from a disaster. They are not needed for initial installation and configuration of the Cluster Platform 220/1000 management server.
Before you attempt to restore the management software environment, you must know your system configuration information and the state of your system backups. See TABLE 2-1 on "Invalid Cross-Reference Format" for information on your customized configuration.
Your system configuration information must include the following:
1. Access the management server console through the terminal concentrator:
# telnet sc3sconf1-tc Trying 192.212.87.62... Connected to sc3sconf1-tc. Escape character is '^]' <CR> Rotaries Defined: cli Enter Annex port name or number: 1 |
2. To issue a Stop-A command to the cluster nodes and to access the OpenBoot PROM (OBP) prompt, position the cursor in the Cluster Console window and enter the <ctrl>] character sequence.
3. This character forces access to the telnet prompt. Enter the Stop-A command, as follows:
telnet> send brk |
4. Boot the system from the CD-ROM:
ok boot cdrom |
The system boots from the CD-ROM and prompts you for the mini-root location
(a minimized version of the Solaris operating environment). This procedure takes approximately 15 minutes.
5. Select a CD-ROM drive from the menu.
Once the Cluster Platform 220/1000 recovery utility has placed a copy of the Solaris operating environment onto a suitable disk slice, the system reboots. You are prompted to specify the CD-ROM drive. Completing this process takes approximately 15 minutes.
6. Install the Solaris operating environment software.
You are prompted to remove CD0 and mount CD1 on the CD-ROM drive. After
CD1 is mounted, press the Return key. The Solaris operating environment files are copied from CD1 onto the management server boot disk. This process takes approximately 20 minutes.
7. Install the second data CD.
When all files are copied from the first data CD, you are prompted to remove CD 1 and mount CD 2 on the CD-ROM drive. After CD 2 is mounted, press the Return key. The software and patch files are copied from CD 2 onto the management server boot disk. When all files are copied from both CDs, the system automatically shuts down. You must reboot the system. This process takes approximately 20 minutes.
Once the management server recovery software is loaded, you must configure the system to match your environment. See Sun Cluster Standard Rack Placement to customize your cluster environment. If the recovery process involves the replacement of cluster nodes, refer to Ethernet IP Address Worksheet to verify that the first cluster node's FC-AL is properly set up.
Copyright © 2002, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.