| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B28286-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B28286-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This section tells you how to refer to schema objects and their parts in the context of a SQL statement. This section shows you:
The general syntax for referring to an object
How Oracle resolves a reference to an object
How to refer to objects in schemas other than your own
How to refer to objects in remote databases
How to refer to table and index partitions and subpartitions
The following diagram shows the general syntax for referring to an object or a part:
database_object_or_part::=
where:
object is the name of the object.
schema is the schema containing the object. The schema qualifier lets you refer to an object in a schema other than your own. You must be granted privileges to refer to objects in other schemas. If you omit schema, then Oracle assumes that you are referring to an object in your own schema.
Only schema objects can be qualified with schema. Schema objects are shown with list item 7. Nonschema objects, also shown with list item 7, cannot be qualified with schema because they are not schema objects. An exception is public synonyms, which can optionally be qualified with "PUBLIC". The quotation marks are required.
part is a part of the object. This identifier lets you refer to a part of a schema object, such as a column or a partition of a table. Not all types of objects have parts.
dblink applies only when you are using the Oracle Database distributed functionality. This is the name of the database containing the object. The dblink qualifier lets you refer to an object in a database other than your local database. If you omit dblink, then Oracle assumes that you are referring to an object in your local database. Not all SQL statements allow you to access objects on remote databases.
You can include spaces around the periods separating the components of the reference to the object, but it is conventional to omit them.
When you refer to an object in a SQL statement, Oracle considers the context of the SQL statement and locates the object in the appropriate namespace. After locating the object, Oracle performs the operation specified by the statement on the object. If the named object cannot be found in the appropriate namespace, then Oracle returns an error.
The following example illustrates how Oracle resolves references to objects within SQL statements. Consider this statement that adds a row of data to a table identified by the name departments:
INSERT INTO departments VALUES ( 280, 'ENTERTAINMENT_CLERK', 206, 1700);
Based on the context of the statement, Oracle determines that departments can be:
A table in your own schema
A view in your own schema
A private synonym for a table or view
A public synonym
Oracle always attempts to resolve an object reference within the namespaces in your own schema before considering namespaces outside your schema. In this example, Oracle attempts to resolve the name departments as follows:
First, Oracle attempts to locate the object in the namespace in your own schema containing tables, views, and private synonyms. If the object is a private synonym, then Oracle locates the object for which the synonym stands. This object could be in your own schema, another schema, or on another database. The object could also be another synonym, in which case Oracle locates the object for which this synonym stands.
If the object is in the namespace, then Oracle attempts to perform the statement on the object. In this example, Oracle attempts to add the row of data to departments. If the object is not of the correct type for the statement, then Oracle returns an error. In this example, departments must be a table, view, or a private synonym resolving to a table or view. If departments is a sequence, then Oracle returns an error.
If the object is not in any namespace searched in thus far, then Oracle searches the namespace containing public synonyms. If the object is in that namespace, then Oracle attempts to perform the statement on it. If the object is not of the correct type for the statement, then Oracle returns an error. In this example, if departments is a public synonym for a sequence, then Oracle returns an error.
If a public synonym has any dependent tables or user-defined types, then you cannot create an object with the same name as the synonym in the same schema as the dependent objects.
If a synonym does not have any dependent tables or user-defined types, then you can create an object with the same name in the same schema as the dependent objects. Oracle invalidates any dependent objects and attempts to revalidate them when they are next accessed.
See Also:
Oracle Database PL/SQL Language Reference for information about how PL/SQL resolves identifier namesTo refer to objects in schemas other than your own, prefix the object name with the schema name:
schema.object
For example, this statement drops the employees table in the sample schema hr:
DROP TABLE hr.employees;
To refer to objects in databases other than your local database, follow the object name with the name of the database link to that database. A database link is a schema object that causes Oracle to connect to a remote database to access an object there. This section tells you:
How to create database links
How to use database links in your SQL statements
You create a database link with the statement CREATE DATABASE LINK. The statement lets you specify this information about the database link:
The name of the database link
The database connect string to access the remote database
The username and password to connect to the remote database
Oracle stores this information in the data dictionary.
When you create a database link, you must specify its name. Database link names are different from names of other types of objects. They can be as long as 128 bytes and can contain periods (.) and the "at" sign (@).
The name that you give to a database link must correspond to the name of the database to which the database link refers and the location of that database in the hierarchy of database names. The following syntax diagram shows the form of the name of a database link:
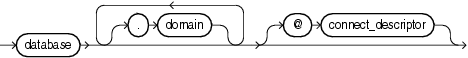
where:
database should specify the name portion of the global name of the remote database to which the database link connects. This global name is stored in the data dictionary of the remote database. You can see this name in the GLOBAL_NAME data dictionary view.
domain should specify the domain portion of the global name of the remote database to which the database link connects. If you omit domain from the name of a database link, then Oracle qualifies the database link name with the domain of your local database as it currently exists in the data dictionary.
connect_descriptor lets you further qualify a database link. Using connect descriptors, you can create multiple database links to the same database. For example, you can use connect descriptors to create multiple database links to different instances of the Oracle Real Application Clusters that access the same database.
The combination database.domain is sometimes called the service name.
Database links are available only if you are using Oracle distributed functionality. When you issue a SQL statement that contains a database link, you can specify the database link name in one of these forms:
The complete database link name as stored in the data dictionary, including the database, domain, and optional connect_descriptor components.
The partial database link name is the database and optional connect_descriptor components, but not the domain component.
Oracle performs these tasks before connecting to the remote database:
If the database link name specified in the statement is partial, then Oracle expands the name to contain the domain of the local database as found in the global database name stored in the data dictionary. (You can see the current global database name in the GLOBAL_NAME data dictionary view.)
Oracle first searches for a private database link in your own schema with the same name as the database link in the statement. Then, if necessary, it searches for a public database link with the same name.
Oracle always determines the username and password from the first matching database link (either private or public). If the first matching database link has an associated username and password, then Oracle uses it. If it does not have an associated username and password, then Oracle uses your current username and password.
If the first matching database link has an associated database string, then Oracle uses it. Otherwise Oracle searches for the next matching (public) database link. If no matching database link is found, or if no matching link has an associated database string, then Oracle returns an error.
Oracle uses the database string to access the remote database. After accessing the remote database, if the value of the GLOBAL_NAMES parameter is true, then Oracle verifies that the database.domain portion of the database link name matches the complete global name of the remote database. If this condition is true, then Oracle proceeds with the connection, using the username and password chosen in Step 2. If not, Oracle returns an error.
If the connection using the database string, username, and password is successful, then Oracle attempts to access the specified object on the remote database using the rules for resolving object references and referring to objects in other schemas discussed earlier in this section.
You can disable the requirement that the database.domain portion of the database link name must match the complete global name of the remote database by setting to FALSE the initialization parameter GLOBAL_NAMES or the GLOBAL_NAMES parameter of the ALTER SYSTEM or ALTER SESSION statement.
See Also:
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for more information on remote name resolutionTables and indexes can be partitioned. When partitioned, these schema objects consist of a number of parts called partitions, all of which have the same logical attributes. For example, all partitions in a table share the same column and constraint definitions, and all partitions in an index share the same index columns.
Partition-extended and subpartition-extended names let you perform some partition-level and subpartition-level operations, such as deleting all rows from a partition or subpartition, on only one partition or subpartition. Without extended names, such operations would require that you specify a predicate (WHERE clause). For range- and list-partitioned tables, trying to phrase a partition-level operation with a predicate can be cumbersome, especially when the range partitioning key uses more than one column. For hash partitions and subpartitions, using a predicate is more difficult still, because these partitions and subpartitions are based on a system-defined hash function.
Partition-extended names let you use partitions as if they were tables. An advantage of this method, which is most useful for range-partitioned tables, is that you can build partition-level access control mechanisms by granting (or revoking) privileges on these views to (or from) other users or roles. To use a partition as a table, create a view by selecting data from a single partition, and then use the view as a table.
Syntax You can specify partition-extended or subpartition-extended table names in any SQL statements in which the partition_extended_name or subpartition_extended_name element appears in the syntax.
partition_extended_name::=
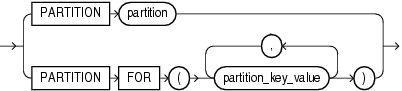
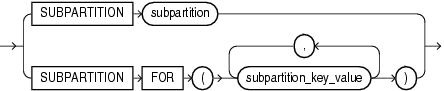
subpartition_extended_name::=
The DML statements INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE and the ANALYZE statement requires parentheses around the partition or subpartition name. This small distinction is reflected in the partition_extension_clause:
partition_extension_clause::=
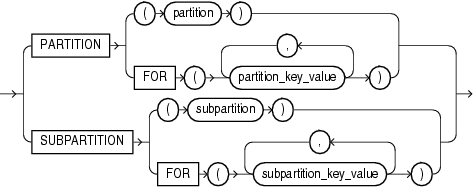
In partition_extended_name, subpartition_extended_name, and partition_extension_clause, the PARTITION FOR and SUBPARTITION FOR clauses let you refer to a partition without using its name. They are valid with any type of partitioning and are especially useful for interval partitions. Interval partitions are created automatically as needed when data is inserted into a table.
For the respective partition_value, specify one value for each partitioning key column. For multicolumn partitioning keys, specify one value for each partitioning key. For composite partitions, specify one value for each partitioning key, followed by one value for each subpartitioning key. All partitioning key values are comma separated. For interval partitions, you can specify only one partition_value, and it must be a valid NUMBER or datetime value. Your SQL statement will operate on the partition or subpartitions that contain the values you specify.
Restrictions on Extended Names Currently, the use of partition-extended and subpartition-extended table names has the following restrictions:
No remote tables: A partition-extended or subpartition-extended table name cannot contain a database link (dblink) or a synonym that translates to a table with a dblink. To use remote partitions and subpartitions, create a view at the remote site that uses the extended table name syntax and then refer to the remote view.
No synonyms: A partition or subpartition extension must be specified with a base table. You cannot use synonyms, views, or any other objects.
The PARTITION FOR and SUBPARTITION FOR clauses are not valid for DDL operations on views.
Example In the following statement, sales is a partitioned table with partition sales_q1_2000. You can create a view of the single partition sales_q1_2000, and then use it as if it were a table. This example deletes rows from the partition.
CREATE VIEW Q1_2000_sales AS SELECT * FROM sales PARTITION (SALES_Q1_2000); DELETE FROM Q1_2000_sales WHERE amount_sold < 0;
To refer to object type attributes or methods in a SQL statement, you must fully qualify the reference with a table alias. Consider the following example from the sample schema oe, which contains a type cust_address_typ and a table customers with a cust_address column based on the cust_address_typ:
CREATE TYPE cust_address_typ
OID '82A4AF6A4CD1656DE034080020E0EE3D'
AS OBJECT
( street_address VARCHAR2(40)
, postal_code VARCHAR2(10)
, city VARCHAR2(30)
, state_province VARCHAR2(10)
, country_id CHAR(2)
);
/
CREATE TABLE customers
( customer_id NUMBER(6)
, cust_first_name VARCHAR2(20) CONSTRAINT cust_fname_nn NOT NULL
, cust_last_name VARCHAR2(20) CONSTRAINT cust_lname_nn NOT NULL
, cust_address cust_address_typ
.
.
.
In a SQL statement, reference to the postal_code attribute must be fully qualified using a table alias, as illustrated in the following example:
SELECT c.cust_address.postal_code FROM customers c; UPDATE customers c SET c.cust_address.postal_code = 'GU13 BE5' WHERE c.cust_address.city = 'Fleet';
To reference a member method that does not accept arguments, you must provide empty parentheses. For example, the sample schema oe contains an object table categories_tab, based on catalog_typ, which contains the member function getCatalogName. In order to call this method in a SQL statement, you must provide empty parentheses as shown in this example:
SELECT TREAT(VALUE(c) AS catalog_typ).getCatalogName() "Catalog Type" FROM categories_tab c WHERE category_id = 90; Catalog Type ------------------------------------ online catalog