Sun Enterprise 10000 Server: Dynamic System Domains
- Introduction
- "Systems within a System"
- Dynamic System Domains--Unlimited Versatility
- Key Features and Benefits
- Reliability, Availability, Serviceability (RAS)
- Example of Sun Enterprise 10000 Server Partitioning Flexibility
- Addressing Business Challenges
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
Data centers today are faced with the overwhelming task of serving established constituencies while addressing the inevitable changes that the information age has prompted. The growing reliance on the inter/intra/extranet combined with the necessity to adopt new applications and apply them throughout the company, locally and globally, promises to strategically benefit corporations as a whole. Against this backdrop, data centers are increasingly chartered with applying existing management principles and practices to the evolving infrastructure.In addition, data center operations are also being impacted by the financial pressures to accommodate the needs of the constituents while maintaining cost accountability that contributes to a company's overall profitability. Operations managers are expected to meet the evolving needs of the organization and their customers in addition to actively contributing to the bottom line.
Today, thousands of users--within and outside the organization--are actively accessing enterprise-wide data, placing huge, unpredictable demands on server and network bandwidth and availability. Simultaneously, data center systems must deliver and maintain the growing volume of data for new decision-based applications, have the capacity to support multi-terabyte data warehouses and support ever expanding, dynamic, global networks. Businesses are finding a greater urgency to rapidly deploy new solutions while maintaining the availability of mission-critical applications, data banks and networking functions.
In short, as these external pressures to expand hardware and software services increase, customers desire flexible solutions to achieve all of these goals. Such solutions would generate increased revenues, improve response time and quality, expand customer and user services, and provide overall competitive advantages.
To adapt to these rapidly changing demands, the hardware and software chosen must be extremely scalable, powerful, and cost-effective. In order to utilize these system attributes to meet today's requirements for flexibility and responsiveness, robust management capabilities are also required. Partitioning is one way to address this need.
Partitioning is the ability to take a single system and dynamically divide it into multiple smaller systems with each partition running its own instance of the operating system. This partitioning flexibility has been a popular and widely used feature exclusive to the mainframe world--until the introduction of the Sun Enterprise 10000 server, the first system to incorporate these features into UNIX� servers.
The Sun Enterprise 10000 server, popularly known as Starfire, is a unique high-performance, highly scalable server that provides, among its many features, mainframe-style partitioning. These partitions, or Dynamic System Domains, allow a single Sun Enterprise 10000 system to be logically divided into multiple servers, creating a "system within a system" in the same cabinet.
The design principles built in to the Sun Enterprise 10000 server allow system administrators to "dynamically" partition (i.e. create, allocate and resize system resources while the system is on-line) from an easy to use system management console without interruption to users and production.
Dynamic System Domains (DSD) are engineered to remain logically isolated from each other within the system, providing a highly secure and reliable environment for running multiple functions simultaneously. Each domain is a self-contained server of one or multiple system boards, containing CPU, memory, I/O, boot-disk and network resources, running Sun's highly robust Solaris Operating Environment software in single or multiple instances.
Sun's Dynamic System Domains provide a multi-purpose single system solution, minimize downtime and allow on-line production maintenance with full software isolation, thus maximizing overall system availability, versatility, and investment protection. The domain, or partitioning, features of the Sun Enterprise 10000 server provide a highly reliable system and cost-effective solution to meet the breadth of demands for today's operation requirements.
Back to top
2. "Systems within a System"
The scope of this white paper focuses on the hardware domain, or partitioning, capabilities of the Sun Enterprise 10000 server. Further information is available in other documents for software partitioning features in the Solaris Operating Environment software which complement the hardware partitioning features discussed here. Finally, the use of partitions and domains are interchanged throughout the focus of this paper.Each Sun Enterprise 10000 system can simultaneously support multiple Dynamic System Domains, or partitions. Each of these domains is essentially a "system within a system", that is, each domain has its own instance of the operating system, as well as its own support resources. The Sun Enterprise 10000 system is currently designed to accommodate up to eight domains. Incremental support will be implemented for additional self-contained domains.
The basic unit of a domain consists of one system board containing up to four processors, four Gigabytes memory and four I/O connections. Each domain operates its own instance of the Solaris Operating Environment software, in addition to different versions or releases of the OS, as well as its own unique name, boot disk, disk connections, memory, CPUs, network, and interconnect access--creating a fully functional, fully isolated partition. Because of this software and hardware independence, all software and nearly all hardware errors in a domain are confined to that domain only and will not affect the rest of the system.
This capability offers the flexibility to configure multiple "systems" within a single server, saving valuable floor space, localizing and simplifying system control, and increasing resource management and availability.
Functions of Dynamic System Domains:
Back to top
- Dynamically Configure; Create, Delete & Resize domains according to workload size, type and schedule
- Isolate domains for workload and workgroup separation
- Specialize by using domains as a dedicated resources for applications with common or distinctly different characteristics, such as those that require dedicated resources for high-availability versus applications that may not require as much compute power, to meet the diverse needs of the entire organization
3. Dynamic System Domains--Unlimited Versatility
Historically, individual UNIX servers were implemented separately for development, testing and production. These isolated systems enabled the development work to continue on a regular schedule without adversely affecting production work. To support these operations, data centers typically housed several discrete servers--one per function.Over the last decade, business have witnessed a tremendous change in computing as companies began to embrace the idea of distributed open systems. The distributed computing model promised a wider range of advantages, the primary being that of price/performance. Increasingly, powerful and affordable server technology gave departments the processing power needed at an affordable price. Distributed systems were also significantly easier to deploy. In parallel, packaged software became more widely embraced, providing a fast, inexpensive solution to data management compared to the legacy applications that were, to this point, inherent in the data center.
However, the very success of distributed systems provided additional complexity, as hardware and software of all types proliferated throughout every area within an organization the management complexity also increased. These distributed systems themselves were also limited in terms of power and manageability, facilitating single application, single server models which exacerbated the very problems they were implemented to solve. Because these distributed, or discrete, servers--and more specifically the packaged software applications they were required to run--required testing and training, and in some cases development or optimization, prior to being brought into production, the issues multiplied. Systems managers began to implement additional hardware dedicated to test and development, while maintaining their primary systems for production (as many as three or four servers per application).
The adoption of distributed systems contributed to floor-space constraints, management complexity and potentially higher cost of ownership. In parallel to distributed system implementations, was the emergence, growth and reliance upon the Internet prompting higher rates of consumer data collection, user access and the need to share data internally and externally to realize true value from both historical and new data being captured. As a result, those organizations that embraced the idea of combining new and legacy data were best positioned to lead and maintain real competitive advantage within their marketspace.
Today, site and user requirements are changing dramatically and the demand for increased connectivity locally, globally and via the Internet has exploded. The discrete server implementations, though highly effective for some applications, have greatly impaired resource manageability, flexibility, availability and accessibility to meet the enterprise-wide demands of an organization. As expansion, combined with the demand for universal connectivity, becomes necessary discrete servers can represent a very expensive solution.
The Sun Enterprise 10000 server was the first system to provide the price/performance found in UNIX systems combined with the rich feature set, such as partitioning, of the mainframe combined with the capacity to host multiple applications, thousands of users and terabytes of data within a single system.
Outlined below are a few ways in which the Sun Enterprise 10000 Dynamic System Domains can be used to increase a site's flexibility, application performance, and system protection through the versatility of partitioning.
Dynamic System Domains address several of the issues of discrete server and legacy system implementations:
Total Cost of Ownership: Cost of system implementation and total cost of ownership (TCO) have become one of the most important issues for businesses seeking to improve competitiveness. While there are many costs associated with system deployment, such as hardware and software procurements, other less visible costs, such as system downtime and management often contribute even more to overall TCO. The ability to implement a single system and dynamically allocate and share resources amongst functions and departments as peak demand requires is one way to reduce cost. Sun's Dynamic System Domains allow the system manager to make better use of resources and services while reducing the management complexity, and more importantly cost, inherent with multiple system implementations.
- Reduced total cost of ownership; centralization of physical resources
- Increased server manageability and flexibility
- Increased availability for the protection of mission-critical applications
- Error protection and application isolation
- Zero latency
Departmental Systems: A single Sun Enterprise 10000 server may be shared by multiple projects or departments, simplifying cost justification and cost accounting requirements. Each department can control system resources to best suit its needs. As those needs change, partition configurations can be dynamically changed without affecting other projects or departments.
Error Protection: Sun's error encapsulation within domains is roughly equivalent to that of mainframe systems. Single bit error or DRAM failure within one domain will not affect other domains. This error protection provides simplified administration. The entire memory data path is protected by error correcting code (ECC) mechanisms, and SIMM organization is specifically designed such that each DRAM chip contributes only one bit to a byte of data. Thus the failure of a DRAM chip causes only correctable single-bit errors. Full ECC or parity data checking on data storage and data paths, and extensive built-in monitoring equipment all permit the Sun Enterprise 10000 server to detect, avoid, and recover from most memory failures automatically.
Software Migration & Upgrades: Dynamic System Domains are an effective means for testing and upgrading systems or applications software to current release versions. Typical migrations and upgrades include the Solaris Operating Environment software, database applications, new administrative environments, and end-user applications. Software may be tested in complete isolation before being deployed enterprise-wide and will not disrupt the existing production environment.
Internet Firewall: Typically, data centers allocate a dedicated and physically detached server to function as the Internet firewall. Because such discrete servers are often under-utilized, any initial cost advantage is greatly reduced over time. Since Dynamic System Domains can be dynamically reconfigured, the Sun Enterprise 10000 server allows system managers to create a firewall domain and adjust its size as Internet demands increase, thereby increasing the system's overall cost effectiveness.
Configuring for Peak Resource Requirements: Dynamic System Domains offer the flexibility needed to run applications that have special or limited resource requirements. Projects that have particularly demanding or limited resource requirements that might overflow onto other applications can be contained within their own system domain. In addition, for those applications that cannot take full advantage of all resources, such as those that do not require scalability, multiple instances of that particular application may be run in separate domains. This flexibility allows full use of resources as necessary and maximizes the systems complete capabilities.
Zero Latency Business Model: Within a matter of minutes a new "server" can be deployed--simply by creating a new Dynamic System Domain. It is instantaneous and eliminates lengthy approval and acquisition processes. The zero latency business model allows administrators to rapidly deploy new applications with moderate time between the actual installation of new resources and its production availability.
Figure-1 Domains and Resource Sharing
Back to top
4. Key Features and Benefits
The following chart illustrates the key features and benefits of the Sun Enterprise 10000 server Dynamic System Domains.
F E A T U R E S B E N E F I T S A single Sun Enterprise 10000 server can be shared by multiple applications, projects or departments through the flexibility of domains Reduced total cost of ownership; simpler capacity planning; simple administration Domains can be dynamically created, modified, resized and removed through a single system management console Increased server manageability, flexibility, and efficient usage of system resources; increases overall system availability On-line dynamic reconfiguration of system domains Data centers can be responsive to changing business needs and rapidly redeploy resources without interrupting production Domain reconfiguration requires no reboot No downtime to impact production Different versions of the Solaris Operating Environment software can run in different domains Domains can be used to test and validate new OS releases and updates Multiple isolated domains Equivalent of multiple systems in a single UNIX server; reduced floor space requirements No physical dependence on board location (i.e. boards do not have to be physically adjacent to be in the same domain) Administrator has extensive control over system configurations, flexibility Complete isolation from software errors in other domains Mission-critical applications are not impacted by applications running within other domains Hardware to support domains has been designed into the Sun Enterprise 10000 system No cost overhead for using domains Unique Dynamic System Domain Implementation
Dynamic System Domains rely on both hardware and software designed specifically for the Sun Enterprise 10000 server. The Sun Enterprise 10000 system's Gigaplane- XB interconnect--the industry's first use of crossbar interconnect for large commercial systems--enables truly self-contained partitions. The Sun Enterprise 10000 server's unique Dynamic Reconfiguration software allows unmatched availability by enabling domain modifications as needed, or "on-the-fly". By combining the versatility of mainframe-style partitions with advanced domain configuration software, the Sun Enterprise 10000 server offers an extremely flexible and powerful hardware partitioning solution.
The hardware technology implemented in the Sun Enterprise 10000 server called domain filtering determines which system boards belong to a given domain. In a system configured as a single domain all boards belong to a single domain where every board can exchange data with every other board. When more than one domain is active, domain filtering isolates domains from each other; that is, no data from within a domain can reach it, except when multiple domains have been explicitly clustered together. Domain filtering effectively eliminates software errors originating in one domain from reaching any other domain. One of the most important features of domain filtering is that it does not add any performance penalties to system performance when Dynamic System Domains are in use.
Back to top
5. Reliability, Availability, Serviceability (RAS)
In addition to the functionality provided with the Sun Enterprise 10000 server's Dynamic System Domains, the system is designed to deliver the reliability, availability and serviceability needed to address the most rigorous data center operations. Assuring continuous access to data and protection against failures is as important, or more so, to mission critical business applications as overall system performance and functionality.Reliability, Serviceability and Availability, or RAS, is the general term used to define the features to assess and measure a given system's ability to operate continuously and reduce service times. The reliability of a system reduces system failures and insures data integrity. A system's serviceability provides for short service cycles when component upgrades are necessary or failures occur. Built-in reliability and high levels of serviceability lead to availability. The availability of a system defines continuous accessibility to the functions and applications supported by the system.
This section details some of the features incorporated into the Sun Enterprise 10000 server that complement the system's RAS and partitioning capabilities. Specific technical detail for these features are provided more in depth within other technical white papers.
On-Line Production Maintenance, Dynamic Reconfiguration & Alternate Pathing
The Sun Enterprise 10000 server is the first UNIX system to incorporate the unique capabilities of system partitioning for flexibility with additional features to provide on- line "no-interrupt" service combined with integral software features such as alternate pathing and dynamic reconfiguration to assure continuous availability and access to data.
Production Maintenance
- Production/No-Interrupt Maintenance, Upgrades & "Hot Swap":
The Sun Enterprise 10000 technology permits on-line upgrades, repair and modification of Dynamic System Domains, while the system is in active use providing no-interrupt maintenance. This is not to be confused with hot-plug terminology, which accommodates hardware changes in inactive parts.
- Dynamic Reconfiguration (DR):
provides maximum flexibility for system configuration, upgrades, and quick recovery from failures.
- Alternate Pathing (AP):
is part of Sun's RAS features that provides higher availability by permitting each server or domain to be configured against the failure of disk arrays, disk and network controllers providing redundant paths to each and provides automatic recognition and failover in the event of disk failures.
- Quick Recovery Business Strategy:
A properly configured Sun Enterprise 10000 server will automatically reconfigure itself to resume execution in the event of a failure. Even the system centerplane, the Gigaplane-XB interconnect, provides redundancy, in that if one half of the centerplane fails the system would automatically reconfigure out that portion of the interconnect, running in a degraded mode while providing access to the full domain configuration implemented on the system prior to error. The server can be configured to provide up to 99.95% availability. This is achieved through a combination of built-in redundancy and alternate pathing features designed to provide the highest level of system availability.The Sun Enterprise 10000 server comes equipped with a comprehensive diagnostic software system and allows a system board to be inserted or removed without powering off the system. This true "hot-swap" procedure is designed for on-line servicing of system boards or for upgrading memory, I/O, or processor configurations. Only the immediate system board and its components are affected.
When bringing the server on-line, the system diagnostics determine which units are available in the Sun Enterprise 10000 server. In the event of a failed component, the Sun Enterprise 10000 server self-test automatically detects and isolates that component and logically disables it for servicing. There are many possible combinations to protect against failures including a series of heuristics, using site-specified parameters, to determine which configuration is to be used in such cases.
Once the component is isolated, the upgrade or replacement board is then inserted and powered on. The system management console runs diagnostics on the new board, after which the system board is logically reattached to the operating system. During this period, the system continues to operate and user applications are unaffected.
Alternate Pathing
Alternate Pathing is a foundation for dynamic reconfiguration, enabling I/O operations to be redirected to the alternate path if the system board serving the primary path must be removed from the configuration.
Similarly, to maintain production, the Sun Enterprise 10000 server features include the ability to configure redundant paths to the network assuring ongoing connectivity to peripherals and production. This feature, known as Alternate Pathing (AP), permits each server to be protected from the effects of failure through providing redundant paths to network controllers and disk arrays. These options increase availability for mission-critical applications and meet high reliability requirements to protect against single points of hard failure.
Alternate Pathing software manages redundant network controllers and I/O. Using Alternate Pathing to oversee two independent controllers, attached to separate system boards, provides end-to-end protection. The system administrator defines the primary and alternate path for each device. If a failure is detected, the system automatically fails-over to the alternate path. These actions take place while the system remains in operation. For supported disk arrays, this can be accomplished without losing any data being transmitted. Once the alternate path is activated, the component may be swapped out or upgraded with the dynamic attach features without interrupting production.
AP and no-interrupt servicing strategies are part of Sun's Reliability, Availability and Serviceability (RAS) features and are unique to the server product suite which can be configured such that virtually no single point of failure exists.
Dynamic Reconfiguration
A major difference in hardware implementations is the amount of dynamic reconfiguration capability. DR requires both hardware and software capabilities.
Complementing Sun's hardware innovations for flexible domains, and inspired by mainframe-features, dynamic reconfiguration (DR) capabilities have been designed into the overall system and software architecture to enable the truly dynamic aspects of domains.
As part of a highly sophisticated software design, DR permits the system administrator to modify the Sun Enterprise 10000 system configuration dynamically. During the reconfiguration of domains, the system remains on-line without affecting users. The Solaris Operating Environment software uses DR to add, modify or remove resources within various domains with uninterrupted service. The result is unlimited, on-line partitioning flexibility, allowing sites to tailor systems for any requirements at any time while retaining high availability.
DR manages the flow of processes and data to and from memory in to preserve application and data integrity when removing or adding components. The entire process is managed from the System Service Processor (SSP), or system management console. When a system board has been newly attached, the board is assigned to a new domain, or added to a running system or domain. Then the alternate pathing is switched back, if appropriate.
Fundamental to the Sun Enterprise 10000 system processes, DR is also integral for boot-time testing, and "no-interrupt" upgrades and servicing. It also is essential to the Sun Enterprise 10000 server's hot-swap, or production maintenance processes, by allowing failed components to be logically deactivated prior to removal while the system remains in production.
DR contains key technology that permits a physical or logical restructuring of a Sun Enterprise 10000 server while the system is in active use. This is sometimes confused with hot-plug capability, which only accommodates hardware changes in inactive parts. DR provides full software support for components to be added or removed, or "hot- swapped" during systems operation, without impacting production work.
Back to top
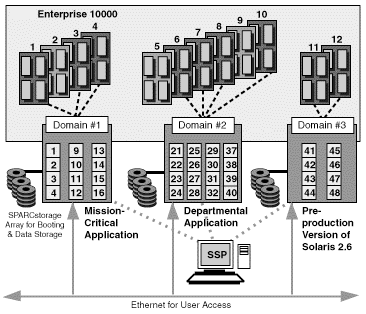
6. Example of Sun Enterprise 10000 Server Partitioning Flexibility
In the following example, Dynamic System Domain #1 has 12 processors running a mission-critical application under the Solaris 2.6 operating environment. The performance on this production domain cannot be degraded by other domains in the system nor can software errors or most hardware errors in other domains affect it.Dynamic System Domain #2 has 16 processors running a departmental application. Because it is self-contained, the performance on this domain is assured and cannot be degraded by other domains in the system. This domain also has its own required boot disk and a network connection.
Dynamic System Domain #3 is being used to run a pre-production version of the Solaris 7 Operating Environment software. This is an 8-processor partition enabling a full test of the OS before it is deployed into production. Notice that any boards may be used to form a domain because there is no physical dependence on board location within a Sun Enterprise 10000 system.
In this illustration, each domain maintains its own boot disk and network connection which increases overall system security and flexibility by isolating the domain.
Figure 2 Dynamic System DomainsError Protection through Domain Isolation
Sun's domain features are comparable to those of the mainframe's logical partitions (LPARS). Sun's domain capabilities provide the same level of protection, for both hardware and software errors.
A Dynamic System Domain is completely shielded from any type of software error from other domains, including those errors generated by a panic condition or a program crash.
In addition, most hardware errors contained within a single domain will not affect another. If memory or processors fail within a domain, any component specific to one domain cannot affect any other domain. There are virtually no types of hardware errors within domains that will affect other domains providing complete isolation and protection for superior system reliability.
Configuring multiple domains allows system administrators to safely test new software, isolate mission-critical applications, create device-specific domains--with the assurance that each domain is fully protected from errors in any other domain. This error isolation dramatically increases the Sun Enterprise 10000 server's overall reliability, availability, and functionality.
Dynamic System Domain Configuration
Although Dynamic System Domains have been designed to offer simple and flexible configurations for a wide variety of applications and functions, careful attention to a site's resource needs and availability will yield optimal performance and availability. Planning and care should be taken to assure that each domain is properly configured with peripherals and adequate memory for the tasks it will be assigned. A system with alternate pathed devices will have these devices attached to two different system boards. To preserve and optimize such alternate paths, the two boards should be configured in the same domain in order to provide the required redundancy. Finally, because partitions stand as a self-contained systems, each domain requires its own boot disk and network connection.
Domain size is limited only by the number of configured system boards--a domain may be as small as a single board or as large as all boards within the system. A system board can currently belong to only one domain at any one time. The Sun Enterprise 10000 server's Dynamic System Domains have been designed to offer extremely flexible configurations– domains can be created dynamically using any available system processor boards; that is, the boards do not have to be physically adjacent to be included in the same domain. For example, Domain #1 could contain boards 2, 5, and 9 while Domain #2 could contain boards 3, 6, 15, and 16.
Domain Management
The System Service Processor (SSP) is the management console through which domains are activated and controlled. By issuing dynamic reconfiguration commands at the SSP through either a graphical (Hostview) or a command-line interface, the administrator can create, modify, or remove domains dynamically. To configure a domain, the administrator first assigns one or more system boards to a domain, with no service interruption to end users. The OS automatically brings the new domain on line, available for immediate use.
Because each domain has its own unique name (hostid), the SSP recognizes it as a completely independent system with its own IP address. Hostview (see figure below) provides simple, graphical representation and control of all domain functions and their associated resources as well as the entire Sun Enterprise 10000 system.
Hostview InterfaceIn addition to local administration, domains can be managed through a remote access console, which allows the system administrator to reside in a location separate from the server itself. This might be a central console room or a location miles away. The remote console software, netcon, makes all SSP functions, including domains, available from a remote location, increasing administrative flexibility and ease of operation.
7. Addressing Business Challenges
Data center applications and implementations are evolving and changing, and in many instances, converging. This section examines some practical implementations for domains that assist in addressing the complexity of new, distributed and mixed application workloads.RDBMS Advantage: The Sun Enterprise 10000 server is a very high-performance, highly scalable, fast-access, shared-memory SMP system. The system is capable of accommodating very large, multi-terabyte database applications. Many of the new applications in use today benefit from the Sun Enterprise 10000 server's domain isolation capabilities. The most important benefits of independent isolation are system and application integrity and availability. Many of the leading relational databases, including Oracle, Informix and Sybase are developed and implemented specifically for SMP environments. When compared with other systems architectures relying on clusters of small nodes running parallel databases, combined with difficult distributed lock-management techniques, the Sun Enterprise 10000 server provides an ideal architecture to accommodate very large database implementations while reducing both the cost and complexity associated with RDBMS installations. Server Consolidation: System domains are key to centralized management and an excellent means of reducing the number of systems that must be managed in an organization. The benefits include easier administration through a single system console, more extensive RAS features, and unparalleled flexibility to freely shift resources from one domain or "server" to another. This is a benefit as applications grow, or when demand reaches peak levels requiring rapid deployment of additional computing resources. Domains also minimize underutilization, inherent with distributed server implementations.Enterprise Resource Planning & Multi-tier Applications: Several types of applications require multi-tiered architectures. In these implementations, the application must be functionally divided. For example, enterprise resource planning (ERP) applications often require a desktop client, a midrange application server, and a powerful database server. Data warehousing applications are often supplemented by smaller data marts. Using Dynamic System Domains, all tiers except the desktop interface may be housed within a single Sun Enterprise 10000 server. The ability to consolidate the tier-layers provides excellent performance and simplifies administration. Data Mining: Most data mining applications transfer data from one database to another over the network, resulting in slowed communications and network bottlenecks. The Sun Enterprise 10000 server's Gigaplane-XB interconnect provides an ideal solution for intensive data mining applications: By configuring two separate Sun Enterprise 10000 system domains to host the source and target databases, the data mining operations can move data at transfer rates significantly higher than 100 BaseT.Data Warehousing: Leadership today demands an in depth and direct understanding of customer trends. More than anytime in the past, companies are aggressively seeking to understand customer patterns and trends to focus their products and services to meet individual customer needs. Targeted marketing and services determine success. Underlying the focus of customer service and targeted marketing is the need to accommodate the volumes of data captured, both new and historical, and the ability to analyze that data. As Web-based applications continue to grow and companies recognize the value of all data, having a system that has the capacity, flexibility, and bandwidth to sort through the data will determine a company's success and competitive advantage. Multiple Environments: Managing multiple and heterogeneous environments and multiple and mixed applications has become standard in today's data centers. Systems must be designed to accommodate these multiple environments and applications. A system must be flexible, highly robust, and accommodate connectivity capabilities to exist within heterogeneous environments. In addition, systems must also have the capability for test and development functions in order to bring new applications and functions on-line without adversely affecting overall production. Systems must also be able to run multiple, and often disparate, applications and allow those disparate applications to share data. Having the capability to meet the demands of multiple environments within a single system greatly improves system response, provides flexible resources, greatly reduces the overall complexity of systems management, and reduces the total cost of ownership. Back to top
- Very Large Database and Data Warehouse
- Server Consolidation
- Multiple Environments and Mixed workloads
- Enterprise Resource Planning
8. Conclusion
An important advantage unique to the Sun Enterprise 10000 server, Dynamic System Domains offer mainframe-like versatility and reliability to UNIX environments.The ability to use easily-configured partitions for a wide range of needs, including hosting multiple testing and production environments in a single server is crucial to the requirements of today's evolving data centers. Using the Sun Enterprise 10000 server for consolidation, data warehousing, on-line transaction processing (OLTP), and efficient data mining and ERP solutions provides data centers with reduced total cost, increased server manageability and flexibility, and increased availability for these critical functions.
By dynamically assigning different functions to different domains as needs change, the Sun Enterprise 10000 server enables maximum utilization, simplifies administrative and operational costs, and significantly reduces the total cost of ownership.
As the pressures to expand hardware, software, and services increase, customers can look to Sun to provide solutions that can grow flexibly to meet all of their business challenges, generate increased revenues, improve response time and quality, expand customer and user services, and provide overall competitive advantage.
Back to top