| Oracle® Database Application Express User's Guide Release 3.0 Part Number B32258-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database Application Express User's Guide Release 3.0 Part Number B32258-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This section describes the steps to migrate applications from Microsoft Access to Oracle Application Express.
This section contains the following topics:
Oracle Application Express Application Migration Workshop (Application Migration) enables you to migrate a Microsoft Access application and generate an Oracle Application Express application from the retrieved objects.
This migration begins with exporting your Microsoft Access metadata, using the Exporter tool together with Oracle Migration Workbench. After that initial step, you want to use Application Migration to review the retrieved objects and resolve any issues regarding invalid objects. As the final step, you have the option of generating either an application based on valid forms and reports or a maintenance application based on valid tables and views.
Once the application is generated, you can take advantage of all the functionality in Application Express to further develop and publish the migrated application.
Forum for Application Migration
In addition to Oracle support, you can post questions on the Microsoft Access Migration to Oracle Application Express:
Before you begin the migration process, verify that your system meets these requirements:
Oracle Application Express version 3.0
You must have installed Application Express 3.0. You use the Application Migration feature within Application Express to download the Exporter tool as well as to migrate Microsoft Access forms and reports to Application Express.
Oracle Migration Workbench version 10.1.0.4.0 or higher (available in English only)
You must have installed Oracle Migration Workbench version 10.1.0.4.0 or higher. You use the Migration Workbench to migrate the Microsoft Access schema and data to Oracle.
Exporter tool version 10.2.0.2.0 (available in English only)
If you are using Oracle Migration Workbench version 10.1.0.4.0, you must install the Exporter tool using the Download Exporter link within Application Express. For instructions, see "Step 1: Export Microsoft Access Metadata".
If you are using a version higher than 10.1.0.4.0, you can access the Exporter directly from Oracle Migration Workbench.
Microsoft Access
Your local system must have Microsoft Access installed, and it must be installed where the Exporter tool and .mdb file reside.
Microsoft Data Access Components (MDAC)
Your local system should have the latest version of Microsoft Data Access Components (MDAC) installed. You can download the latest version from the Microsoft Web site.
Printer
Your local system must have a printer installed so that a report can be opened in design view. This is a requirement for exporting your Reports information from an .mdb file.
Analyze your .mdb file before you export your database. Follow the instructions in the next section.
Analyze Your .MDB File in Microsoft Access
Using Microsoft Access, you should analyze your .mdb file before you export your database. Performing these steps will minimize errors in the migration.
In Microsoft Access, analyze the objects in your .mdb file:
From the Microsoft Access menu bar, select Tools, Analyze, and then Documenter.
Select the All Object Types tab, and then click the Select All button to select all the objects within the application for analysis.
Remove or resolve any erroneous objects reported by the Documenter.
Ensure the application contains no missing references:
In Microsoft Access, launch the design IDE (press Alt+F11 keys).
From the menu bar, select Tools and then References.
Remove or resolve any missing references.
Ensure the application compiles successfully:
From the menu bar in the IDE view, select Debug and then Compile.
Resolve any reported errors.
Perform a compact and repair on the database:
From the menu bar in Microsoft Access, select Tools, Database Utilities, and then Compact and Repair Database.
Ensure that all linked tables are valid links:
From the menu bar in Microsoft Access, select Tools, Database Utilities, and then Linked Table Manager.
Verify that all links are up-to-date and pointing to an existing .mdb file that is not read-only.
Before you begin
Read "Preparation Checklist for Migrating Applications".
To migrate applications from Microsoft Access to Oracle Application Express, you need to perform the steps described in this section. This graphic outlines the entire process:
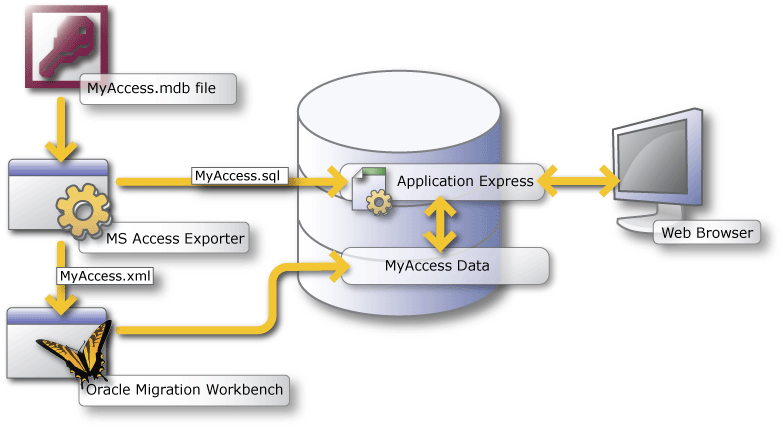
The migration process consists of the following steps:
Step 1: Export Microsoft Access Metadata
Step 2: Migrate the Microsoft Access Database to Oracle
Step 3: Create an Oracle Application Express Workspace
Step 4: Create a Migration Project
Step 5: Review Your Retrieved Objects
Step 6: Generate the Oracle Application Express Application
Important:
You must follow the steps in the exact sequence presented in this section.To export your metadata from Microsoft Access, download the correct version of the Exporter tool, as explained in this section. Then, run the Exporter and extract the metadata from the Microsoft Access .mdb file. The metadata contains the necessary database and application schema information.
The export process creates two output files:
database (.xml file)
application (.sql file)
Downloading the Exporter Tool
Note:
Follow the instructions in this section if you are using Oracle Migration Workbench version 10.1.0.4.0. If you are using a higher version, access the Exporter directly from Oracle Migration Workbench and skip this task.To download the Exporter tool for Microsoft Access:
Log in to Oracle Application Express 3.0.
Under Migrations on the right side of the Workspace home page, click Application Migrations.
Under Tasks on the right side of the page, click Download Exporter for Microsoft Access.
In the Download column, click the zip file that corresponds to your version of Microsoft Access. For example, download the omwb2003.zip file if you are using Microsoft Access 2003.
Save the file.
Unzip the file. You must replace the following files with the updated versions in the msaccess_exporter directory where you unzipped Oracle Migration Workbench:
schema.dtd file
Exporter tool file: omwb<version>.mde
online help file: omwb.chm
Be sure to invoke the export from this directory.
Exporting Your Metadata
To export your metadata, follow the instructions found in the help file for the Exporter tool. To find the instructions, do one of the following:
Launch the Exporter tool, and click the Help button.
Open the help file (omwb.chm) contained in the Exporter zip file.
The instructions appear in the topic called Exporter Overview.
To migrate the Microsoft Access database to Oracle:
Log in to Oracle Migration Workbench 10.1.0.4.0 or higher.
Load the database metadata (.xml file) resulting from Step 1. This migrates the schema and data to Oracle.
If you are using version 10.1.0.4.0 of Oracle Migration Workbench, make sure that you have updated the /omwb/msaccess_exporter folder with the latest version of the schema.dtd from the zip file in Step 1.
Important:
When using the Oracle Migration Workbench, you must verify that the Destination Database in the Migration wizard is the same instance where Application Express 3.0 is installed. If you do not, you are not able to complete the next step.For more information about Oracle Migration Workbench, see:
The method for creating workspaces depends on your Application Express configuration. For more information, see "Quick Start".
While creating your workspace, be sure to associate it with the newly created schema from Step 2.
If you are new to Application Express, also see the Oracle Database 2 Day + Application Express Developer's Guide.
To create a migration project:
Log in to Oracle Application Express.
Make sure you log in to the workspace you created for your migration project (Step 3).
Under Migrations on the right side of the Workspace home page, click the Application Migrations link.
On the Application Migrations page, click Create Project.
The Create Migration Project wizard appears. Note that the steps included in the wizard appear in a flowchart on the left of the page.
Enter the project details:
Project Name - Enter a unique name. You might want to use the same name as the Microsoft Access .mdb file you used to create the project.
Type - Select Access.
Description - Enter a meaningful description for this project. You might want to describe the Microsoft Access .mdb file that you used to create the project.
Migration Export File - Click Browse and select the .sql file created by the Exporter tool for Microsoft Access.
Schema - Select the schema.
The default schema is the schema associated with your workspace. If more than one schema is associated with your workspace, all associated schemas appear in the select list, arranged in alphabetical order. When this situation exists, select the schema associated with the SQL script you want to upload.
Click Next.
Review the project details, and click Finish.
The project page appears.
See Also:
"About the Project Page", "Step 5: Review Your Retrieved Objects", and "How to Migrate Your Applications"The project page initially shows a high-level overview of the Microsoft Access objects retrieved from your Microsoft Access database.
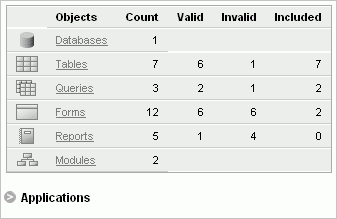
Specifically, the project page shows the status of these objects in your database:
tables
queries (now Oracle views)
forms
reports
Additionally, for reference purposes only, the project page shows:
databases
modules
pages
Note that your project might not include all object types. The project page lists only object types that exist in your database.
After you generate applications from this migration project, an application list is created on the project page. To review the list, click Applications. This opens the list box where you can review application information or run an application.
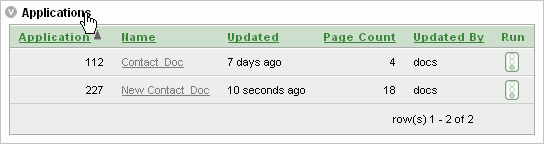
Next, you want to select the objects to include in the migration. The initial list consists of the Microsoft Access application metadata that is retrieved, both valid and invalid.
To include an object, it must have a status of Valid. By default, all objects with a Valid status are selected. From within Application Migration, you can fix objects identified as invalid so that they can be included. Since the Application Migration also identifies tables without primary keys and objects without user interface defaults, you can correct those situations to maximize application design recovery.
Tip:
Extensive Oracle documentation is available for broadening your knowledge of database concepts and objects. For example, to learn more about primary keys and constraints, see Oracle Database Concepts or Oracle Database Application Developer's Guide - Fundamentals, which you can download from:This section includes these topics:
Next, review the Oracle tables retrieved from the Microsoft Access database. Application Migration identifies invalid tables without primary keys as well as those without user interface defaults, which you can add before migrating.
After you update the tables, select the ones you want to include in the migration. If you do not include a table, all forms and reports based on the table are excluded from the migration.
To review retrieved tables:
From the project page, click Tables.
The Tables page appears, showing the status of the objects ready for migration.
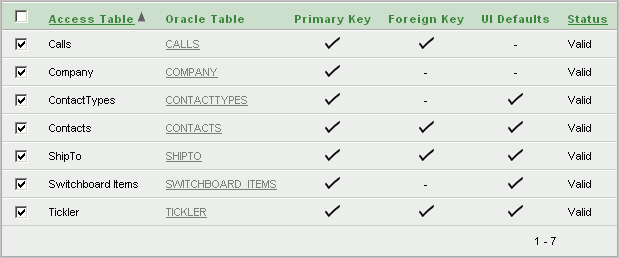
For each Microsoft Access table, the Tables page shows:
Oracle Table - The corresponding Oracle table, which defaults to the Microsoft Access table name in all capital letters.
Note that the name might also differ from the original one because of the collision management facility in Oracle Migration Workbench. For information about naming guidelines and restrictions, click Help in Oracle Migration Workbench and go to the Frequently Asked Questions section.
If the Microsoft Access object was not successfully migrated to Oracle, then this field will not have a corresponding Oracle table name. Instead, it will contain a link to a page where you can create a corresponding Oracle table.
Primary Key - Indicates if a primary key exists for the table.
A table without a primary key is considered invalid in Application Migration. You can create a primary key at this point. All tables you want to migrate should have a primary key.
Foreign Key - Indicates if a foreign key exists for the table.
If you know a relationship exists between two tables, you should create a foreign key. You can do this through SQL Workshop, a component of Application Express. For more information about SQL Workshop, see the Oracle Application Express User's Guide or the Application Express online Help.
UI Defaults - Indicates if user interface defaults are set for the table.
User interface defaults are used by Application Express to populate initial values for region and item properties. Using user interface defaults provides consistency across multiple applications or across multiple pages in an application.
Status - Table status as either Valid or Invalid.
Only valid tables can be included in the migration.
To create a table:
On the Tables page, click the link in the Oracle Table column for the table you want to create.
The Object Browser opens.
Click the Create button.
From the list of object types, select Table.
Follow the on-screen instructions.
To add a primary key:
On the Tables page, click the Oracle table name.
In the Tasks list on the right, click Create Primary Key.
For Constraint Details, fill in the information.
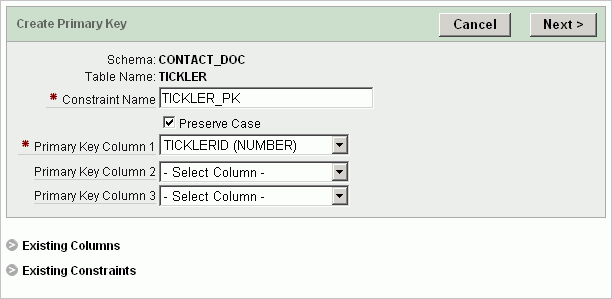
Tip:
To review the list of existing columns or constraints, click the Existing Columns or Existing Constraints links.Click Next.
Confirm the information and click Finish.
To add an index:
On the Tables page, click the Oracle table name.
In the Tasks list on the right, click Create Index.
Select the type of index you want to create on this table.
For indexing NUMBER, VARCHAR, and DATE, select Normal. For indexing CLOB columns, select Text.
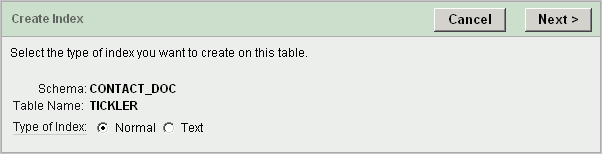
Click Next.
For Index Definition, fill in the information.
The following graphic shows the fields to fill out if you selected Normal as the type of index.
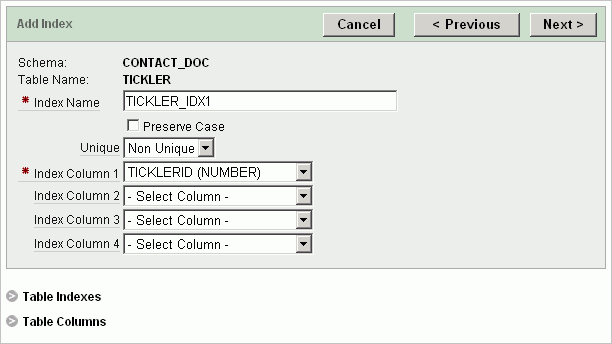
Tip:
To review the list of existing table indexes or columns, click the Table Indexes or Table Columns links.Click Next.
Confirm the information and click Finish.
To set user interface defaults:
On the Tables page, click the Oracle table name.
In the Tasks list on the right, click UI Defaults.
On the UI Defaults page, click Create Defaults.
The Table Defaults page appears, listing column information as it will appear in forms and reports. Note that you are now working within Application Builder, the component of Application Express where you can build and modify your applications.
To edit the information, click Grid Edit. You can update the column label, change the sequence the columns will appear by default, and so on.
Click Apply Changes to save your updates.
To include tables in the migration, select them in the left column.
Click Apply Changes to save your selections.
Next, review the queries retrieved from the Microsoft Access export. Application Migration identifies invalid queries as well as those without user interface defaults, which you can set before migration.
After you update the views, select the ones you want to include in the migration. If you do not include a query, any forms or reports based on the query are excluded from the migration.
To review retrieved queries:
From the project page, click Queries.
The Queries page appears, showing the status of the objects ready for migration.
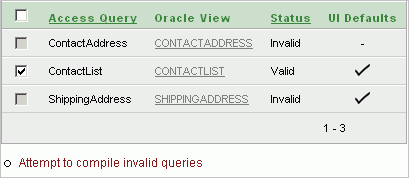
For each Microsoft Access query, the Queries page shows:
Oracle View - The corresponding Oracle view, which defaults to the Microsoft Access query name in all capital letters.
If the Microsoft Access object was not successfully migrated to Oracle, then this field will not have a corresponding Oracle view name. Instead, it will contain a link to a page where you can create a corresponding Oracle view.
Status - Query status as either Valid or Invalid.
Only valid queries can be included in the migration.
UI Defaults - Indicates if user interface defaults are set for the query.
User interface defaults are used by Application Express to populate initial values for region and item properties. Using user interface defaults provides consistency across multiple applications or across multiple pages in an application.
To run a bulk process that attempts to compile all invalid queries, click Attempt to compile invalid queries.
Using this option can validate some queries that show a status of invalid when initially migrated.
To create a view:
On the Queries page, click the link in the Oracle View column for the view you want to create.
The Object Browser opens.
Click the Create button.
From the list of object types, select View.
Follow the on-screen instructions.
To edit a query:
On the Queries page, click the Oracle view you want to edit.
Click Compile to find the invalid part of the query.
The Microsoft Access Query syntax appears in the edit window. It may require some modification to make it valid Oracle syntax.
Click Access Query to review the initial query and compare it to the converted query.
Click Edit.
Update the query and recompile it.
When it is validated, click the Queries breadcrumb.
To include this validated query, select it in the left column on the Queries page and click Apply Changes.
To set user interface defaults:
On the Queries page, click the Oracle view.
In the Tasks list on the right, click UI Defaults.
On the UI Defaults page, click Create Defaults.
The Table Defaults page appears, listing column information as it will appear in forms and reports. Note that you are now working in Application Builder, the component within Application Express where you build and modify applications.
To edit the information, click the Grid Edit button.
You can update the column label, change the sequence the columns will appear by default, and so on.
Click Apply Changes to save your updates.
To return to the Application Migration, click the Home breadcrumb. Then, select the Application Migrations link on the right, select your migration project, and click Queries.
To include queries in the migration, select them in the left column.
Click Apply Changes to save your selections.
Next, review the forms retrieved from the Microsoft Access export. Application Migration identifies invalid forms and lists additional information, such as the form's source type and source name.
For valid forms with a source type of table, you can select the type of object you want the form to become within Application Express: form (default), report and form, or tabular form.
Microsoft Access forms based on a query are migrated to Application Express forms. Microsoft Access forms based on a SQL query are migrated to Application Express reports.
After you update the forms, select the ones you want to include in the migration.
To review retrieved forms:
From the project page, click Forms.
The Forms page appears, showing the status of the objects ready for migration.
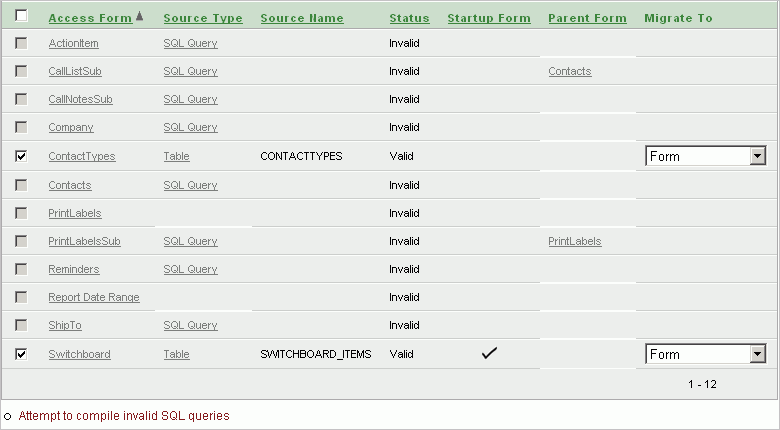
For each Microsoft Access form, the Forms page shows the following information, if available:
Source type:
Table
Query - The Oracle view that was migrated from the Microsoft Access query.
SQL Query - The original Microsoft Access SQL query that the Microsoft Access form is based on. Note that this query has not been parsed by the Oracle Migration Workbench. Therefore, you might need to edit it to make it valid Oracle SQL syntax.
Nothing - The form has no underlying source type.
Source name - The Oracle table or view name if the source type is a table or query.
Status - Form status as Valid or Invalid. The source of the form must have a status of Valid before you can select it for migration.
A form's status is based on two factors: status of its underlying source object and inclusion of the source object in the migration. Specifically, a form has a status of valid if either one of these situations exists:
Its Source Type object (table, query, or SQL query) is valid, and it has been included in the migration. Its check box is enabled and can be selected.
Its Source type object has a status of valid, but the source object was not included in the migration. Its check box is disabled.
A form has a status of invalid if either one of these situations exists:
No Source Type is listed. Its check box is disabled.
Its Source Type object (table, query, or SQL query) is invalid. Its check box is disabled.
Startup form - Identifies the form that displays when you open your Microsoft Access database.
Parent form - Indicates the form/subform relationship that existed in your Microsoft Access database. For example, the CallListSub form shows Contacts as its Parent Form.
Migrate to: Form, Tabular Form, or Report and Form - The select list appears if the source type is a valid table.
To run a bulk process that attempts to compile all invalid SQL queries, click Attempt to compile invalid SQL queries.
Using this option can validate some SQL queries that show a status of invalid. Note that SQL queries from Microsoft Access forms are not loaded into the Oracle Migration Workbench, and are therefore not parsed.
To edit a SQL query:
On the Forms page, click the SQL Query you want to edit.
Click Validate to find the invalid part of the SQL query.
Click Edit.
Update the query and validate it.
When it is validated, click the project name breadcrumb.
To include the validated query, click Forms on the project page to go to the Forms page. Then select the newly validated query in the left column and click Apply Changes.
To edit a query:
On the Forms page, click Query for the form you want to edit.
Click Compile to find the invalid part of the query.
Click Access Query to review the initial query and compare it to the converted query.
Click Edit.
Update the query and recompile it.
When it is validated, click the Queries breadcrumb.
To include this validated query, select it in the left column on the Queries page and click Apply Changes.
To review details about a form, click the link in the Access Form column.
To include forms in the migration, select them in the left column.
Click Apply Changes to save your selections.
Next, review the reports retrieved from the Microsoft Access export. Application Migration identifies invalid reports and lists additional information, such as the report's source type and source name.
After you update the reports, select the ones you want to include in the migration. To include a report, the source of the report must have a status of Valid.
To review retrieved reports:
From the project page, click Reports.
The Reports page appears, showing the status of the objects ready for migration.
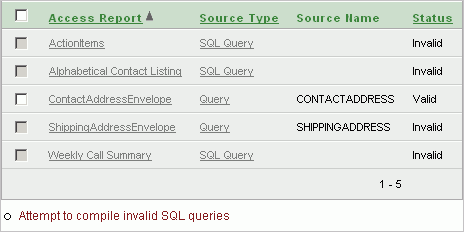
For each Microsoft Access report, the Reports page shows the following information, if available:
Source type:
Table
Query - The Oracle view that was migrated from the Microsoft Access query.
SQL Query - The original Microsoft Access SQL query that the Microsoft Access form is based on. Note that this query has not been parsed by the Oracle Migration Workbench. Therefore, you might need to edit it to make it valid Oracle SQL syntax.
Nothing - The report has no underlying source type.
Source name
Status of the report: Valid or Invalid. The source of the report must have a status of Valid before you can select it for migration.
A report's status is based on two factors: status of its underlying source object and inclusion of the source object in the migration. Specifically, a report has a status of valid if either one of these situations exists:
Its Source Type object (table, query, or SQL query) is valid, and it has been included in the migration. Its check box is enabled and can be selected.
Its Source type object has a status of valid, but the source object was not included in the migration. Its check box is disabled.
A report has a status of invalid if either one of these situations exists:
No Source Type is listed. Its check box is disabled.
Its Source Type object (table, query, or SQL query) is invalid. Its check box is disabled.
To run a bulk process that attempts to compile all invalid SQL queries, click Attempt to compile invalid SQL queries.
Using this option can validate some SQL queries that show a status of invalid. Note that SQL queries from Microsoft Access forms are not loaded into the Oracle Migration Workbench and are therefore not parsed.
To edit a SQL query:
On the Reports page, click the SQL Query link you want to edit.
Click Validate to find the invalid part of the SQL query.
Click Edit.
Update the query and validate it.
When it is validated, click the project name breadcrumb.
To include the validated query, click Reports on the project page to go to the Reports page. Then select the newly validated SQL query in the left column and click Apply Changes.
To edit a query:
On the Reports page, click Query for the report you want to edit.
Click Compile to find the invalid part of the query.
Click Access Query to review the initial query and compare it to the converted query.
Click Edit.
Update the query and recompile it.
When it is validated, click the Queries breadcrumb.
To include this validated query, select it in the left column on the Queries page and click Apply Changes.
To review details about a report, click the link in the Access Report column.
To include reports in the migration, select them in the left column.
Click Apply Changes to save your selections.
From the project page, you can drill down to see information about the database, modules, and pages for the migration project.
Database - Displays summary information about the Microsoft Access database, including the full path and size of the .mdb file.
Modules - Displays the Visual Basic Code, enabling you to extract embedded SQL statements for you to use or edit in your Application Express application.
Pages - Displays information for reference purposes.
After validating and updating objects, you now need to generate the application in Application Express. You can create an application based on valid forms and reports, or a maintenance application based on valid tables and views.
When creating an application, a home page is defined by default. You have the option to create additional blank pages so that you can introduce further navigation possibilities.
You can then choose which user interface theme your application should be based on. By default, the application uses one level of tabs.
As a shortcut, you can also set some application defaults. These defaults are used whenever you create new applications.
Setting Up Application Defaults
To set up application defaults (optional):
On the right side of the project page, click Generate Application Defaults in the Tasks list.
Select the options you want to use as defaults.
For information, click Help or click the item label. Clicking the item label opens a separate window describing the item and its options.
Click Apply Changes.
The project page appears.
Generating Applications
To generate either type of application:
On the right side of the project page, click one of the following in the Tasks list:
Generate Application - This option generates an application based on the forms and reports you selected to include.
Generate Maintenance Application - This option generates an application based on the tables and queries you selected to include.
In the Selected Application Objects section, you can customize specific pages.
For example:
To rename a page, click the page link and enter the new name on the New Page Definition page that appears.
To select the type of navigation on the application's home page, click the Home Page link.
On the New Page Definition page that appears, select Vertical Unordered List with Bullets, Vertical Images List or Horizontal Images List for Navigation.
To display an image on a parent page, click the page link.
On the New Page Definition page that appears, go to the Page Icon field and select the image you want to appear on that page. You can either select an image from the select list or click the Find icon (flashlight) to open a page of options.
Repeat this step for each parent page. If you do not explicitly select an image for a page, the default image appears for that page.
Note that for the image to appear in your application, you must have selected either Vertical Images List or Horizontal Images List for the Home page navigation.
To add a blank page to the application, scroll down to the Add Page section and click Add Page.
Note that the new page appears at the bottom of the list in the Selected Application Objects section.
Click Next to select a theme for the application, or click Create to skip the theme selection step.
If you skip the theme step, the default is used.
Select a theme for the application and click Next.
A theme is a collection of templates that define the layout and style of an application, including buttons and pages.
Confirm your selections and click Create.
To preview the application, click Run Application.
Log in using your Application Express workspace credentials.
Your application now appears as a separate application in Application Express.
To customize your application, scroll down to the Developer toolbar and click Edit Application.
You might want to do the following customizations immediately after you generate your application:
Rename the application. Each application has a unique ID, but the migration project name becomes the application name by default. To more easily identify an application, you might want to change its name to something more meaningful by editing the application attributes.
Change the authentication scheme. By default, the authentication scheme is Application Express authentication. You can change this by editing the application attributes.
See Also:
For instructions on editing application attributes, adding pages, deploying your application, and so on, see the Oracle Database Application Express User's Guide or the Application Express online Help.If you upload a newer version of the export file and create a new migration project from that, you might want to delete the previous migration project.
When you delete a migration project, you delete only the metadata associated with the migration project. Deleting a migration project does not delete or impact applications you have generated from the project or any objects, such as tables or views, in the schemas associated with your workspaces.
To delete a migration project:
Log in to Oracle Application Express.
Under Migrations on the right side of the Workspace home page, click the Application Migrations link.
On the Application Migrations page, click the project you want to delete.
On the project page, click Delete Project from the Tasks list on the right.
Click the Delete Project button and confirm the deletion.