| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Purpose
Use the CREATE INDEXTYPE statement to create an indextype, which is an object that specifies the routines that manage a domain (application-specific) index. Indextypes reside in the same namespace as tables, views, and other schema objects. This statement binds the indextype name to an implementation type, which in turn specifies and refers to user-defined index functions and procedures that implement the indextype.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Data Cartridge Developer's Guide and Oracle Database Concepts for more information on implementing indextypes |
Prerequisites
To create an indextype in your own schema, you must have the CREATE INDEXTYPE system privilege. To create an indextype in another schema, you must have the CREATE ANY INDEXTYPE system privilege. In either case, you must have the EXECUTE object privilege on the implementation type and the supported operators.
An indextype supports one or more operators, so before creating an indextype, you must first design the operator or operators to be supported and provide functional implementation for those operators.
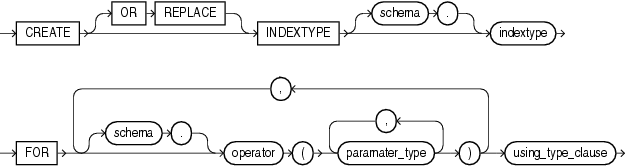
Syntax
create_indextype::=

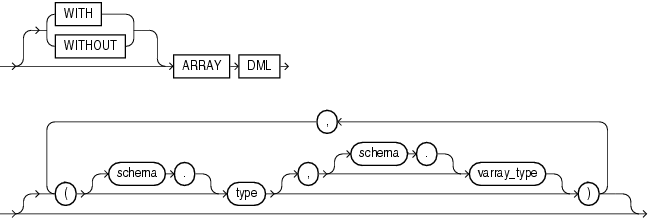
array_DML_clause ::=
Semantics
schema
Specify the name of the schema in which the indextype resides. If you omit schema, then Oracle Database creates the indextype in your own schema.
indextype
Specify the name of the indextype to be created.
Use the FOR clause to specify the list of operators supported by the indextype.
For schema, specify the schema containing the operator. If you omit schema, then Oracle assumes the operator is in your own schema.
For operator, specify the name of the operator supported by the indextype.
All the operators listed in this clause must be valid operators.
For parameter_type, list the types of parameters to the operator.
The USING clause lets you specify the type that provides the implementation for the new indextype.
For implementation_type, specify the name of the type that implements the appropriate Oracle Data Cartridge Interface (ODCI).
You must specify a valid type that implements the routines in the ODCI.
The implementation type must reside in the same schema as the indextype.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Data Cartridge Developer's Guide for additional information on this interface |
Use this clause to let the indextype support the array interface for the ODCIIndexInsert method.
type and varray_type If the datatype of the column to be indexed is a user-defined object type, then you must specify this clause to identify the varray varray_type that Oracle should use to hold column values of type. If the indextype supports a list of types, then you can specify a corresponding list of varray types. If you omit schema for either type or varray_type, then Oracle assumes the type is in your own schema.
If the datatype of the column to be indexed is a built-in system type, then any varray type specified for the indextype takes precedence over the ODCI types defined by the system.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Data Cartridge Developer's Guide for more information on the ODCI array interface |
Example
Creating an Indextype: Example The following statement creates an indextype named position_indextype and specifies the position_between operator that is supported by the indextype and the position_im type that implements the index interface. Please refer to "Using Extensible Indexing" for an extensible indexing scenario that uses this indextype:
CREATE INDEXTYPE position_indextype FOR position_between(NUMBER, NUMBER, NUMBER) USING position_im;