| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Syntax
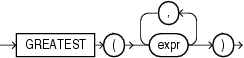
Purpose
GREATEST returns the greatest of the list of one or more expressions. Oracle Database uses the first expr to determine the return type. If the first expr is numeric, then Oracle determines the argument with the highest numeric precedence, implicitly converts the remaining arguments to that datatype before the comparison, and returns that datatype. If the first expr is not numeric, then each expr after the first is implicitly converted to the datatype of the first expr before the comparison.
Oracle Database compares each expr using nonpadded comparison semantics. Character comparison is based on the value of the character in the database character set. One character is greater than another if it has a higher character set value. If the value returned by this function is character data, then its datatype is always VARCHAR2.
|
See Also: Table 2-10, "Implicit Type Conversion Matrix" for more information on implicit conversion, "Floating-Point Numbers" for information on binary-float comparison semantics, and "Datatype Comparison Rules" |
Examples
The following statement selects the string with the greatest value:
SELECT GREATEST ('HARRY', 'HARRIOT', 'HAROLD')
"Greatest" FROM DUAL;
Greatest
--------
HARRY