| Oracle® Database Recovery Manager Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10770-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database Recovery Manager Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10770-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
delete::=
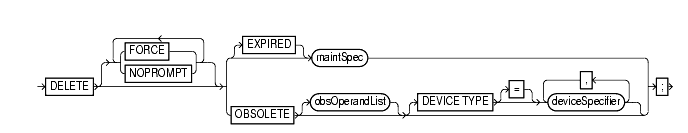
maintSpec::=
To delete physical backups and copies as well as do the following:
DELETEDWhen running RMAN interactively, DELETE displays a list of the files and prompts you for confirmation before deleting any file in the list. When reading commands from a command file, RMAN will not prompt for confirmation.
The repository record for a backup can sometimes fail to reflect the physical status of the backup. For example, you back up a log to disk and then use an operating system utility to delete the file. If you do not run the CROSSCHECK command to update the repository, and if you then run DELETE against the backup, then the repository shows that the object is AVAILABLE while the object is in fact missing. The following table indicates the behavior of DELETE in such situations.
| See Also:
"BACKUP" to learn about the |
DELETE command can delete usable backups and copies from prior incarnations.DELETE is used with a file that is disk-only (that is, an ARCHIVELOG, DATAFILECOPY, CONTROLFILECOPY). Otherwise, you must use a manual or automatic maintenance channel.
If you use DELETE on files that are not disk-only, and if you have objects created on device types that are not configured for automatic channels, then run manual maintenance commands on these channels. For example, if you created a backup using an sbt channel, but have only a DISK channel automatically configured, you must manually allocate an sbt channel for DELETE.
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Deletes specified files (whether or not they exist on the media) and removes repository records. RMAN ignores any I/O errors for the deleted objects. RMAN displays the number of deleted objects at the end of the job. |
|
|
Deletes specified files without first listing the files or prompting for confirmation. The By default, |
|
|
Removes only files whose status in the repository is If for some reason a backup or copy marked |
|
Deletes files output by the |
|
|
|
Deletes backups and datafile copies recorded in the RMAN repository that are obsolete, that is, no longer needed. In addition to obsolete datafile backups, RMAN deletes obsolete archived logs and archived log backups. RMAN determines which backups and copies of datafiles are no longer needed, which in turn determines when logs (and backups of logs) are no longer needed. RMAN considers the creation of a datafile is as a backup when deciding which logs to keep. RMAN first uses the options that you specify with obsOperandList to determine what is obsolete. If you do not specify options in obsOperandList, then RMAN uses the options specified in |
|
Specifies the criteria for determining which backups and copies are obsolete. See Also: "obsOperandList" |
|
|
|
Restricts the deletion to obsolete backups and copies created on the specified device type only. See Also: "deviceSpecifier" |
The following example uses a configured sbt channel to check the media manager for expired backups of the tablespace users that are more than one month old and removes their catalog records:
CROSSCHECK BACKUPSET OF TABLESPACE users DEVICE TYPE sbt COMPLETED BEFORE 'SYSDATE-31'; DELETE NOPROMPT EXPIRED BACKUPSET OF TABLESPACE users DEVICE TYPE sbt COMPLETED BEFORE 'SYSDATE-31';
The following example deletes backups and copies that are not needed to recover the database to a random point within the last week. RMAN also deletes archived redo logs that are no longer needed:
DELETE NOPROMPT OBSOLETE RECOVERY WINDOW OF 7 DAYS;
The following example deletes backups and copies (including archived redo logs) that have already been backed up at least twice to tape:
DELETE NOPROMPT BACKUP BACKED UP 2 TIMES TO DEVICE TYPE sbt; DELETE NOPROMPT COPY BACKED UP 2 TIMES TO DEVICE TYPE sbt;
The following example attempts to delete the backup set copy with tag weekly_bkup:
DELETE NOPROMPT BACKUPSET TAG weekly_bkup;
However, RMAN displays a warning because the repository shows the backup set as available, but the object is not actually available on the media:
RMAN-06207: WARNING: 1 objects could not be deleted for SBT_TAPE channel(s) due RMAN-06208: to mismatched status. Use CROSSCHECK command to fix status List of Mismatched objects ========================== Object Type Filename/Handle --------------- --------------------------------------------------- Backup Piece 0id270ud_1_1
The following command forces RMAN to delete the backup set:
DELETE FORCE NOPROMPT BACKUPSET TAG weekly_bkup;