| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Purpose
Use the ROLLBACK statement to undo work done in the current transaction or to manually undo the work done by an in-doubt distributed transaction.
|
Note: Oracle recommends that you explicitly end transactions in application programs using either aCOMMIT or ROLLBACK statement. If you do not explicitly commit the transaction and the program terminates abnormally, then Oracle Database rolls back the last uncommitted transaction. |
|
See Also:
|
Prerequisites
To roll back your current transaction, no privileges are necessary.
To manually roll back an in-doubt distributed transaction that you originally committed, you must have the FORCE TRANSACTION system privilege. To manually roll back an in-doubt distributed transaction originally committed by another user, you must have the FORCE ANY TRANSACTION system privilege.
Syntax
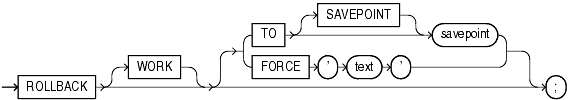
Semantics
The keyword WORK is optional and is provided for SQL standard compatibility.
Specify the savepoint to which you want to roll back the current transaction. If you omit this clause, then the ROLLBACK statement rolls back the entire transaction.
Using ROLLBACK without the TO SAVEPOINT clause performs the following operations:
Ends the transaction
Undoes all changes in the current transaction
Erases all savepoints in the transaction
Releases any transaction locks
Using ROLLBACK with the TO SAVEPOINT clause performs the following operations:
Rolls back just the portion of the transaction after the savepoint
Erases all savepoints created after that savepoint. The named savepoint is retained, so you can roll back to the same savepoint multiple times. Prior savepoints are also retained.
Releases all table and row locks acquired since the savepoint. Other transactions that have requested access to rows locked after the savepoint must continue to wait until the transaction is committed or rolled back. Other transactions that have not already requested the rows can request and access the rows immediately.
You cannot manually roll back an in-doubt transaction to a savepoint.
Specify FORCE to manually roll back an in-doubt distributed transaction. The transaction is identified by the text containing its local or global transaction ID. To find the IDs of such transactions, query the data dictionary view DBA_2PC_PENDING.
A ROLLBACK statement with a FORCE clause rolls back only the specified transaction. Such a statement does not affect your current transaction.
ROLLBACK statements with the FORCE clause are not supported in PL/SQL.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Heterogeneous Connectivity Administrator's Guide for more information on distributed transactions and rolling back in-doubt transactions |
Examples
The following statement rolls back your entire current transaction:
ROLLBACK;
The following statement rolls back your current transaction to savepoint banda_sal:
ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT banda_sal;
See "Creating Savepoints: Example" for a full version of the preceding example.
The following statement manually rolls back an in-doubt distributed transaction:
ROLLBACK WORK
FORCE '25.32.87';