| PL/SQL User's Guide and Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10807-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| PL/SQL User's Guide and Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10807-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
The SET TRANSACTION statement begins a read-only or read-write transaction, establishes an isolation level, or assigns the current transaction to a specified rollback segment. Read-only transactions are useful for running multiple queries against one or more tables while other users update the same tables. For more information, see "Setting Transaction Properties with SET TRANSACTION".
Syntax
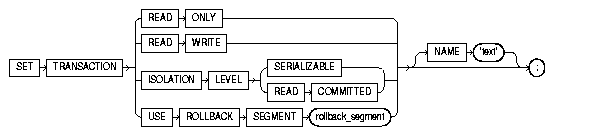
Keyword and Parameter Description
Establishes the current transaction as read-only, so that subsequent queries see only changes committed before the transaction began. The use of READ ONLY does not affect other users or transactions.
Establishes the current transaction as read-write. The use of READ WRITE does not affect other users or transactions. If the transaction executes a data manipulation statement, Oracle assigns the transaction to a rollback segment.
Specifies how to handle transactions that modify the database.
SERIALIZABLE: If a serializable transaction tries to execute a SQL data manipulation statement that modifies any table already modified by an uncommitted transaction, the statement fails.
To enable SERIALIZABLE mode, your DBA must set the Oracle initialization parameter COMPATIBLE to 7.3.0 or higher.
READ COMMITTED: If a transaction includes SQL data manipulation statements that require row locks held by another transaction, the statement waits until the row locks are released.
Assigns the current transaction to the specified rollback segment and establishes the transaction as read-write. You cannot use this parameter with the READ ONLY parameter in the same transaction because read-only transactions do not generate rollback information.
Specifies a name or comment text for the transaction. This is better than using the COMMIT COMMENT feature because the name is available while the transaction is running, making it easier to monitor long-running and in-doubt transactions.
Usage Notes
The SET TRANSACTION statement must be the first SQL statement in the transaction and can appear only once in the transaction.
Example
The following example establishes a read-only transaction:
BEGIN
COMMIT; -- end previous transaction
SET TRANSACTION READ ONLY;
FOR person IN (SELECT last_name FROM employees WHERE ROWNUM < 10)
LOOP
dbms_output.put_line(person.last_name);
END LOOP;
dbms_output.put_line('------------------');
FOR dept IN (SELECT department_name FROM departments WHERE ROWNUM < 10)
LOOP
dbms_output.put_line(dept.department_name);
END LOOP;
COMMIT; -- end read-only transaction
END;
/
Related Topics