This article discusses best practices for deploying the Sun Storage Automated Diagnostic Environment (StorADE) utility to monitor Sun supported storage devices in the data center. The purpose of this to provide StorADE installation and configuration best practice recommendations that result in the optimal use of the StorADE utility based on the storage topology of a given environment
The first part of this article provides a high-level overview of the StorADE utility, and describes which environments are best served by the utility. This information is relevant for IT architects, or anyone looking for ways to improve the reliability, availability, and serviceability (RAS) of their Sun storage solutions.
The second part of this article provides step-by-step installation and configuration information that can be used by an administrator, or anyone tasked with deploying the StorADE utility. The information provides helpful suggestions for making the most of your StorADE deployment, whether the environment contains complex storage area networks (SANs), or straightforward direct-connect devices.
The following topics are covered in this article:
"Sun StorADE 2.2 Features"
"Installing StorADE"
Sun StorADE 2.2 Features
StorADE is a utility provided by Sun that enables centralized monitoring of most Sun storage product offerings. For a complete listing of supported products, see TABLE 1.
StorADE uses well-established Solaris™ Operating System (OS) facilities, such as crond and inetd, for operation. StorADE use and administration is performed using standard browsers such as Netscape Navigator™, Mozilla, or Microsoft Internet Explorer. Refer to the StorADE release notes for supported versions.
StorADE 2.2 is available at no cost as a download from: http://www.sun.com/downloads. For details on downloading this utility, see "To Download the StorADE Package" on page 14.
The Sun StorADE utility has the following features:
-
Enables centralized monitoring for all supported devices and hosts through a browser-based user interface (BUI). You view the devices by topology or by list (FIGURE 8).
Monitors storage devices, providing a health status at the storage subsystem, device, and field replaceable unit (FRU) levels.
Delivers notification of key events in the following ways (based on configuration):
Local notification – Events can be communicated to a local administrator (through email), or to local management software (such as Sun™ Management Center, or through scripts to third-party applications).
Remote notification – Events are communicated to Sun using Sunsm Remote Services Net Connect service (SRS Net Connect) for improved serviceability.
Maintains logs and provides on-demand reports for storage device events.
Provides storage diagnostics that enable a point-and-click approach to fault isolation.
Offers expert advice and troubleshooting for actionable events.
Checks the software, hardware, and firmware revisions of all monitored storage devices and hosts.
Provides detailed storage device FRU reports (FIGURE 1) that describe the device type, vendor, model, and revision number information.
Offers a secure-mode configuration for environments where security is a concern.
FIGURE 1 shows the StorADE FRU and model summary page.
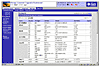 FIGURE 1
StorADE FRU and Model Summary
FIGURE 1
StorADE FRU and Model Summary
Supported Storage Products
Once installed, StorADE monitors the local and remote storage products listed in TABLE 1.
NOTE
The product list in TABLE 1 is up to date as of the time of publication. Refer to the StorADE release notes for updates.
TABLE 1 Supported Products
|
Sun StorEdge™ products |
Sun StorEdge A5000 array (14 slot) |
|
|
Sun StorEdge A5200 array (22 slot) |
|
|
Sun StorEdge A3500-FC array |
|
|
Sun StorEdge T3 array (F/W 1.17 or greater) |
|
|
Sun StorEdge T3+ array (F/W 2.0 or greater) |
|
|
Sun StorEdge 6120 array |
|
|
Sun StorEdge FC Tape T9840 |
|
|
Sun StorEdge FC Tape T9840B |
|
|
Sun V880 Server |
|
|
Sun StorEdge D2 Array |
|
|
Sun Internal Fibre Channel disks (E3500) |
|
|
Sun StorEdge 3510 FC array |
|
|
Sun StorEdge 3900/6900 series |
|
|
Sun StorEdge 6320 system |
|
|
Sun StorEdge Solution racks |
|
SAN-type products |
Sun StorEdge Network FC Switch-8 and Switch-16. |
|
|
Sun StorEdge Network 2-Gbit FC Switch-8, Switch-16 and Switch-64. |
|
|
Brocade Silkworm 2400/2800 FC Switch |
|
|
Brocade Silkworm 3200/3800/12000 FC Switch |
|
|
Brocade 3900 32-Port FC Switch |
|
|
McData ED6064 FC Switch |
|
|
McData ES3232 FC Switch |
|
|
McData 4500 2GB 24-Port FC Switch |
|
|
McData 6140 FC Switch |
|
|
Inrange FC 9000 Director FC Switch |
|
Host bus adapters |
Sun StorEdge PCI FC-100 Host Adapter |
|
|
Sun StorEdge SBus FC-100 Host Adapter |
|
|
Sun StorEdge PCI Dual Fibre Channel Host Adapter |
|
|
Sun StorEdge 2 Gb FC PCI Single-Channel Network Adapter |
|
|
Sun StorEdge 2 Gb FC PCI Dual-Channel Network Adapter |
|
|
Sun StorEdge 2 Gb FC cPCI Dual-Channel Network Adapter |
|
|
JNI FC Host Adapter |
TABLE 2
How StorADE Works
The StorAdE software is installed on one or more servers in a data center. During the installation you are prompted to configure the server as a StorADE master agent or slave agent. The following points and FIGURE 2 describe the roles of each.
Master Agent – serves the following functions:
Aggregates all monitoring data collected from master and slave monitoring activities.
Monitors devices out of band (monitors the device using the device Ethernet interface).
Monitors devices in band (monitors the device using the device Fibre Channel or SCSI data path.)
Monitors various Solaris OE log files for storage-related events.
Stores StorADE events in StorADE log files.
Sends notification of key events to local personnel using simple mail transfer protocol (SMTP).
Optionally, sends notification of key events to Sun using SRS Net Connect. For details on SRS Net Connect services, go to http://www.sun.com/srs.
Provides the centralized BUI for StorADE administration and for checking monitoring data.
Can be used as a management station (performs no monitoring; used only to aggregate data, send notifications, and provide the BUI).
Slave Agent – serves as another StorADE resource with the following functions:
Provides the ability to scale the StorADE functionality according to needs.
Monitors devices out of band (monitors the device using the device Ethernet interface).
Monitors devices in band (monitors the device using the device Fibre Channel or SCSI data path.)
Monitors its own Solaris OE log files for storage-related events.
Stores StorADE events in StorADE log files.
Forwards actionable events and alerts from all monitoring activities to the master agent.
Can be installed on a log host, and used only as a central repository for log files.
Installing the StorADE package on a server adds a cron entry to the server and a StorADE-specific http service. The cron wakes up the StorADE agent periodically (the default is five minutes) to probe devices and monitor log files.
The StorADE user interface is accessed through a browser. Pointing a browser at a slave host port 7654 (or port 7443 for secure configurations) redirects it to the master server automatically.
The StorADE Service Advisor feature provides content that includes a summary of the event, its probable-cause, as well as a recommended corrective action.
 FIGURE 2 StorADE
Configuration Components
FIGURE 2 StorADE
Configuration Components
Deploying StorADE
There are a variety of ways to deploy the StorADE utility in your environment. Your best practice StorADE deployment depends on the type of storage you plan to monitor and the topology of your enterprise.
This article outlines four sample monitoring solutions for entry-level and mid-range servers. These solutions correspond with the overall environment (topology) rather than with particular applications running in it. You can use any of these deployment solutions as is, or tailor them to fit your exact needs. Examples of customization opportunities include adding additional slaves or data hosts to distribute load and scale the StorADE utility.
Review the four sample monitoring solutions to identify which solution meets your needs, and use the configuration to plan your StorADE deployment. Large complex environments might benefit by using a combination of the given solutions.
Solution A – Single Agent with In-Band and Out-of-Band Devices
The configuration shown in FIGURE 3 is made up of a single master agent installed on one host that is used to monitor everything—in-band devices, out-of-band devices, and log files. The master provides the console and is responsible for sending all notifications. The host must have access to all log files, all out-of-band devices, and connectivity for notifications (such as email and SRS Net Connect).
 FIGURE 3
StorADE Deployment for Solution A
FIGURE 3
StorADE Deployment for Solution A
TABLE 3 Pros and Cons for Solution A
|
StorADE Configuration |
1 Master |
|
Pros |
This configuration is the simplest and easiest to implement. |
|
Cons |
StorADE has a single point of failure. If the master host goes down, no monitoring or notifications take place. All monitoring is performed by one host. Depending on the number of devices monitored, this configuration might reach saturation, or become negatively affected by a bottleneck (in the host's network interface, for example). |
If your site includes multiple hosts and only one agent is installed, the topology will be incomplete. Consider Solution B if a complete topology is important. If array log files are stored on a separate host, consider Solution C or D.
Solution B – Master and Slave Configuration With In-band and Out-of-band Devices
The configuration shown in FIGURE 4 uses one master host that monitors in-band and out-of-band devices, provides the console, and sends notifications. The slave host is used to monitor in-band host bus adapters (HBAs). Log files are managed by the master and the slave hosts. This solution provides a more complete SAN topology because there is an agent on multiple hosts. This solution is well adapted to sites that have multiple hosts with multiple log files.
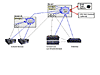 FIGURE 4
StorADE Deployment for Solution B
FIGURE 4
StorADE Deployment for Solution B
TABLE 4 Pros and Cons for Solution B
|
StorADE Configuration |
1 Master 1 or more Slaves |
|
Pros |
This configuration provides some redundancy. If one of the StorADE hosts is down, the others continue to monitor devices. The slave host provides log monitoring for out-of-band devices and in-band HBA monitoring. |
|
Cons |
StorADE is more complex to install than in Solution A. |
Solution C – Master and Slave With In-Band and Out-of-band Devices and a Loghost
The configuration shown in FIGURE 5 uses a master host to monitor in-band devices, out-of-band devices, and slaves. A slave is added to monitor HBAs and log files, with another slave installed (as a data host) on a log host server to capture log messages from the Sun StorEdge T3 arrays. For sites where a separate host is used to store log files, this solution can be used to relay the log information to the master agent. Otherwise, Solution C is the same as Solution B.
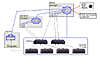 FIGURE 5
StorADE Deployment for Solution C
FIGURE 5
StorADE Deployment for Solution C
TABLE 5 Pros and Cons for Solution C
|
StorADE Configuration |
1 Master (in-band and out-of-band access) 1 or more Slaves (for in-band coverage only) 1 Slave (for log hosting only) |
|
Pros |
You get the same advantages as Solution B, with the addition of a data host that provides log monitoring of out-of-band devices. |
|
Cons |
StorADE is more complex to install than in Solution A or B. |
Solution D – Management Station Configuration
The configuration shown in FIGURE 6 uses the master host to receive monitoring information for out-of-band devices from slaves. The master provides the console and sends all notifications. Slaves are needed to monitor HBAs and log files. Multiple slaves are used to scale the monitoring activities. One slave is installed on a log host for log monitoring. When a large number of slaves are present, there is often a need for a separate master to aggregate the slaves and reach the remote monitoring notifiers. When the master's only functions are aggregating the slaves, providing the BUI, and sending notifications, it is often referred to as a management station. This solution is necessary if none of the slaves have access to the remote notification providers (such as SRS Net Connect). This situation can be common on large sites with multiple subnets.
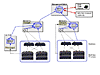 FIGURE 6 StorADE
Deployment for Solution D
FIGURE 6 StorADE
Deployment for Solution D
TABLE 6 Pros and Cons for Solution D
|
StorADE Configuration |
1 Master (out-of-band log host) 1 or more Slaves 1 Slave (for the data host) |
|
Pros |
You get the benefits of a management station where you have a central point for the BUI, aggregation of slave monitoring, and logging of out-of-band devices. This configuration provides the best monitoring topology of all four solutions. |
|
Cons |
This is the most complex solution to install. |
Enabling Security
No matter which deployment solution you use, if security is a concern, you should install all agents with security enabled. StorADE is installed with security turned on when you run the ras_install installation script and answer yes to the security question.
The StorADE secure installation uses the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol for transmission of information between the master and slaves, and between the master and the StorADE BUI. The highest grade encryption (RC4 with 128-bit secret key) is used. The StorADE package includes a default certificate that expires in 2008. This certificate is located in /opt/SUNWstade/System/certificate.pem.
When secure mode is used, the default URL (port 7653) is used when a redirect occurs. The non-secure URL is http://hostname:7654. Site-specific certificates can be created with the openssl utilities (part of the public domain OpenSSL product).
StorADE also supports user-level security. StorADE user accounts are created by the root (ras) login. Each user is assigned user privileges based on one of the following roles:
guest – can read StorADE data
admin – can read StorADE data and make StorADE configuration modifications
expert – can run StorADE reports and diagnostics
test – can run StorADE diagnostics
ras – has all the privileges of all the roles (the root equivalent for the StorADE utility)
Each login account allows the user to log in to StorADE with their own login and password, and results in the user having a restricted set of functions available in the BUI.
Installing StorADE
This section describes how to install and configure the StorADE utility with best practice recommendations.
Installation Overview
The following list describes the high-level tasks you perform when installing StorADE. Step-by-step instructions for each task are provided in subsequent sections.
Download the Sun StorADE package from the Sun Download Center.
If you are upgrading from StorADE 2.1 to StorADE 2.2, remove the StorADE 2.1 software before you install the StorADE 2.2 package.
Identify the hosts you plan to use as the StorADE master and slaves. Take note of the solutions described in "Deploying StorADE" on page 7, and the system requirements described in TABLE 7.
Install the StorADE package as a master or slave based on your desired deployment configuration. Perform this task for each master and slave in your environment.
Apply the StorADE patch. Perform this task for each master and slave in your environment.
Initialize the StorADE configuration using the ras_install script. Perform this task for each master and slave in your environment.
Use the StorADE BUI to configure the StorADE Environment to suit your monitoring needs. Perform this task for each master and slave in your environment.
Verify StorADE functionality. Perform this task for each master and slave in your environment.
To Download the StorADE Package
In a browser, go to the Sun Download Center: http://wwws.sun.com/software/download/sys_admin.html
Scroll down the page to the Storage Management section.
Select the Download link for Storage Automated Diagnostic Environment 2.2.
On the Storage Automated Diagnostic Environment Global Release page, select the Download link.
If you are not already registered at the Sun Download Center, register now.
You must be registered at the Sun Download Center before you can download the scripts and tools. If this is your first visit, select Register now. You only have to register once, and it's free. Whenever you come back to the Download Center, just enter your user name and password to log in.
Log in to the Sun Download Center.
Read and accept the License Agreement.
Download the StorADE compressed tar file to your system.
Uncompress and untar the StorADE file.
SUNWstade – The StorADE package
StorADE documentation – the user's guide and release notes are located in the download_directory/SUNWstade/reloc/SUNWstade/docs directory
Copy the SUNWstade directory to each host for which you plan to install a StorADE master or slave agent.
Perform the download according to the download procedures presented by your browser.
Example:
# zcat SUNWstade_2.2.00.03.tar.Z | tar xvf -
After untarring, you will have the following StorADE items:
To Upgrade from StorADE 2.1
The recommended best practice for upgrading StorADE is to remove any previously installed StorADE software. The StorADE configuration and historical monitoring data is kept in /var/opt and is preserved by default during package removal. Master StorADE installations should always be at the latest revision.
Log in as root.
Run the pkgrm command as follows:
# pkgrm SUNWstade
To Identify the Hosts You Plan to Use as StorADE Hosts
Assess your needs based on the type of storage devices you want to monitor.
Make sure each host for which StorADE will be installed meets the requirements listed in TABLE 7.
See "Deploying StorADE" on page 7.
TABLE 7 StorADE System Requirements
|
Category |
Requirement |
|
CPU Platform |
Sun SPARC system |
|
Operating Environment |
Solaris 9 OE Solaris 8 4/01 OE (or above) Make sure you have the latest recommended OS, security, and SAN patches installed. |
|
Browser |
Netscape 4.47, 6.x, 7.x Internet Explorer 5.x, 6.x |
|
Perl |
5.005 or 5.006 (visit http://www.perl.com/pub/language/info/software.html) Once the proper version ins installed, create a symbolic link of the executable to /usr/bin/perl. |
|
SendMail |
Only necessary on the StorADE master host |
|
Disk space |
50 MByte available in /opt for binaries and system libraries. 25 MByte available in /var/opt. This accommodates monitoring of 100 devices. Add 100 KByte for each additional device. |
Refer to the StorADE release notes for the latest information on host requirements.
To Install StorADE on a Host
Log in as root.
Change to the directory where you copied the installation package.
Install the package using the standard Solaris pkgadd command:
Answer the prompts for the License Agreement.
# pkgadd -d . SUNWstade
To Install the StorADE Patch
Use the patchadd command to install the StorADE patch.
# patchadd 114590-xx
You can use the PatchPro utility to check patch levels and to download the latest patches from Sun.
To Initialize the StorADE Configuration
Start the StorADE initialization script in one of the following ways:
To initialize a StorADE master host:
To initialize a StorADE slave host:
# /opt/SUNWstade/bin/ras_install -m -S Y -c
# /opt/SUNWstade/bin/ras_install -s master_IPaddress -S Y -c
TABLE 8 ras_install Options
|
Option |
Description |
|
-m |
Initialize host as a StorADE master. |
|
-s master_IPaddress |
Initialize host as a StorADE slave. Replace master_IPaddress with the IP address of the StorADE master host. |
|
-S Y | N |
Specifies the security mode in one of the following ways: Y – Configure the StorADE host to use secure communications. This is the recommended best practice. N – Configure the StorADE host to use non-secure communications. |
|
-c |
Enable the crontab entry. |
To Configure the StorADE Environment
In a browser, go to the StorADE Master URL: http://master_IPaddress:7654
Log in to StorADE.
username = ras
password = agent
-
Under Basic Installation Steps (FIGURE 7) configure the StorADE environment by selecting each of the eight links (left to right) as described in the following steps:
Select Review Site Info.
Select Review Hosts.
By default, most Device Categories are checked (enabled). There is no harm in leaving the settings like this.
Set the polling interval. The default is 5 minutes.
Select Monitor In-Band data path. This ensures FC Counters are collected from the HBA to the storage link.
Set the messages log location for host and T3.
Select Discover Devices.
By product category.
By subnet search (used for Ethernet and SNMP-capable devices).
(Best Practice) Devices From IP – edit the /etc/deviceIP.conf file and list your devices, then select Devices From IP.
Select Setup Email.
Select Setup Notifications.
Choose encrypted email.
Click the checkbox to select Active.
Click Update.
Select Create Topology.
Select Review Config.
Finish the StorADE installation by selecting Start Agents.
The initial login is:
Best Practice: Change the ras password.
The initial StorADE page (FIGURE 7) is displayed.
 FIGURE 7 Initial
StorADE Page
FIGURE 7 Initial
StorADE Page
Enter the name of your company in the Customer Name field.
The Site Name can be your location (for example, North Data Center). This convention allows for multiple sites under a single company name.
Tips:
Devices can be found in the following ways:
Click Add to Configuration.
Input the passwords for all monitored devices that have passwords (switches, Sun StorEdge T3 arrays, and so on) into Maintain Devices.
This configuration is for local notification, and can be configured to send the notification to email or to a pager.
This is for the alert stream to Sun Microsystems when a device has an event.
Best Practice recommendations:
If you cannot create a topology, the problem might be due to out of date patches. In this case, run the StorADE Revision Check routine (available under the Diagnosis Tab) to get a revision report.
Once Topologies are created (indicated by Done), they can be viewed under Monitor Topology.
This runs a quick check for basic StorADE configuration parameters.
The monitoring process starts. FIGURE 8 shows an example of the StorADE BUI with monitoring underway.
 FIGURE 8 StorADE
BUI During Monitoring
FIGURE 8 StorADE
BUI During Monitoring
Once StorADE is installed, initialized, and configured, you can find details on how to use StorADE in the Storage Automated Diagnostic Environment 2.2 User's Guide. This guide is installed on each StorADE host, and is also available at: http://docs.sun.com.
To Verify StorADE Functionality
Usually you can tell if a StorADE host is functioning by viewing the various StorADE tabs in the StorADE BUI. If you want to further investigate StorADE functionality, the following steps describe how to check the fundamental StorADE infrastructure.
Log in to the StorADE host as root.
Verify the StorADE crontab entry as follows:
Verify the web server installation as follows:
(Best Practice) Run the agent from the command line to verify output:
# crontab -l 0,5,10,15,20,25,30,35,40,45,50,55 * * * * /opt/SUNWstade/bin/rasagent -c >> /opt/SUNWstade/log/cron.log 2>&1
# grep ras /etc/services rashttp2 7654/tcp # Rasagent service # grep ras /etc/inetd.conf rashttp2 stream tcp nowait root /opt/SUNWstade/bin/rashstart rashstart -d /opt/SUNWstade
# /opt/SUNWstade/bin/rasagent -d2
StorADE generates lots of messages. At this point you soul watch for errors indicating that StorADE is not able to function. Other errors might be an indication of a storage problem, in which case StorADE is doing its job, and the messages help you isolate the problem.
To Uninstall StorADE
If for some reason you need to uninstall StorADE, perform the following steps:
As root, use the pkgrm command to remove the StorADE utility:
(Optional) Perform the following command to remove the StorADE configuration database:
# pkgrm SUNWstade
This removes the StorADE utility software, but does not remove your StorADE configuration database.
# rm -rf /var/opt/SUNWstade
Related Resources
The following URLs provide additional information about the topics covered in this article:
Sun Download Center (to download StorADE): http://wwws.sun.com/software/download/sys_admin.html
Sun StorADE Utility web site (for overview): http://www.sun.com/storage/software/storage_mgmt/autodiagnostic
Sun Storage Automated Diagnostic Environment 2.2 Release Notes: http://www.sun.com/products-n-solutions/hardware/docs/pdf/817-0194-10.txt
Sun Storage Automated Diagnostic Environment 2.2 User's Guide (200 page PDF file): http://www.sun.com/products-n-solutions/hardware/ docs/pdf/817-0192-11.pdf
Sun SRS Net Connect web site (for information about Sun's web-based system management services): http://www.sun.com/srs
About the Authors
Mike Monahan is a Field Service Development (FSD) engineer for the RAS Engineering department in Sun's Network Storage division. Mike's primary focus is on developing the StorADE utility, and bringing in storage telemetry from Sun customer sites. The telemetry data is used by Sun Service engineers to assist with customer storage resolutions. Prior to joining the FSD team, Mike spent several years as a backline storage engineer, and most recently as a storage specialist for the Sun Restoration Services Storage Team. Mike is certified in Sun data management, backup and recovery, and storage area network architecture.
Christian Cadieux is a staff engineer based in Broomfield, CO. Christian is the lead developer for the Sun StorADE product line (includes StorADE and RasAgent), and received the 2002 Chairman's Award of Innovation for the development of StorADE. Christian received a B. S. in Computer Systems from Montreal University. He has worked in the computer industry for 15 years, and has experience in a variety of fields including e-commerce ordering and hotel reservation systems.
Accessing Sun Documentation
You can view, print, or purchase a broad selection of Sun documentation, including localized versions, at: http://www.sun.com/documentation
To reference Sun BluePrints™ OnLine articles, visit the Sun BluePrints OnLine web site at: http://www.sun.com/blueprints/online.html
