| Oracle® Database 2 Day DBA 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B28301-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database 2 Day DBA 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B28301-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
As part of a backup strategy, you need to manage database backups. A related task is managing the record of those backups in the RMAN repository. Oracle Enterprise Manager Database Control (Database Control) simplifies these tasks.
An essential part of a backup and recovery strategy is managing backups after you create them. Backup management includes deleting obsolete backups and performing periodic checks to ensure that backups are available and usable.
You can perform backup management tasks from the Manage Current Backups page. This page has two subpages: Backup Sets and Image Copies. Both pages have similar purposes: listing backups based on the record in the RMAN repository and enabling you to manage the backups.
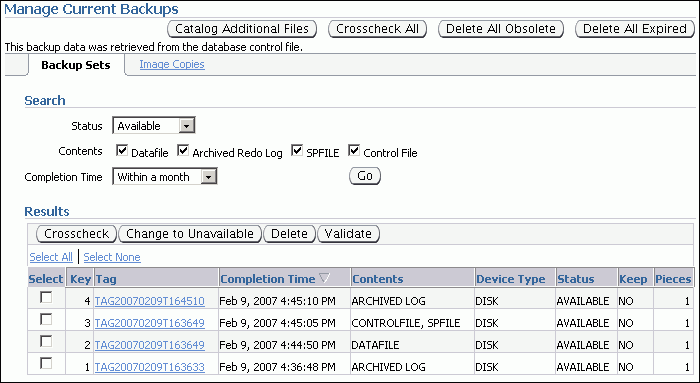
A backup recorded in the RMAN repository has one of the following status values:
Available, meaning that the backup is still present on disk or tape, as recorded in the repository
Expired, meaning that the backup no longer exists on disk or tape, but is still listed in the repository
Unavailable, meaning that the backup is temporarily not available for data recovery operations (because, for example, it is stored on a tape that is stored offsite or on a disk that is currently not mounted)
Backups can also be obsolete. An obsolete backup is, based on the currently configured retention policy, no longer needed to satisfy data recovery goals.
Maintenance tasks that you can perform in Database Control include the following:
Viewing details about your backups
Cross-checking your repository, which means checking whether or not backups listed in the repository exist and are accessible, and marking as expired any backups not accessible at the time of the cross-check
Deleting the record of expired backups from your RMAN repository
Deleting obsolete backups from the repository and from the backup media
Validating backups to ensure that a given backup is available and not corrupted
Note:
If a backup no longer exists, immediately delete the backup record from the RMAN repository. Without an accurate record of available backups, you may discover that you no longer have complete backups of your database when you perform recovery.As with the backup and restore commands in Database Control, the commands to cross-check, delete, and change the status of backups are translated to RMAN commands. The commands are submitted as RMAN jobs that can be run immediately or be scheduled. Some tasks, such as periodic cross-checks of your backups, should be among the regularly scheduled components of your backup strategy.
If you use a flash recovery area for backup storage, then many maintenance activities are reduced or eliminated. The automatic disk space management mechanisms delete backups and other files as needed, thereby satisfying disk space demands for ongoing database operations without compromising the retention policy.
Cross-checking a backup synchronizes the physical reality of backups with their logical records in the RMAN repository. For example, if a backup on disk was deleted with an operating system command, then a cross-check detects this condition. After the cross-check, the RMAN repository correctly reflects the state of the backups.
Backups to disk are listed as available if they are still on disk in the location listed in the RMAN repository, and if they have no corruption in the file header. Backups on tape are listed as available if they are still on tape. The file headers are not checked for corruption. Backups that are missing or corrupt are listed as expired.
To cross-check individual files:
On the Database Home page, click Availability to display the Availability subpage.
In the Backup/Recovery section, click Manage Current Backups.
The Manage Current Backups page appears.
Search for the backup sets or image copies whose contents you want to cross-check.
In the Results section, select each backup to be included in the cross-check operation.
Database Control does not support selecting both image copies and backup sets for a cross-check within a single operation.
Click Crosscheck at the top of the Results list.
After a confirmation page is displayed, Database Control performs the cross-check.
To cross-check all files:
On the Database Home page, click Availability to display the Availability subpage.
In the Backup/Recovery section, click Manage Current Backups.
The Manage Current Backups page appears.
In the Manage Current Backups page, click Crosscheck All.
The Crosscheck All: Specify Job Parameters page appears. You can schedule the cross-check to run now or later, or specify regularly scheduled cross-checks.
Click Submit Job.
Note:
Cross-checking all backups in the RMAN repository may take a long time, especially for tape backups. A cross-check of all files, unlike cross-checking individual files, is handled as a scheduled job.This procedure corresponds to the RMAN CROSSCHECK command. See Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide for details.
Deleting expired backups removes from the RMAN repository those backups that are listed as EXPIRED. Expired backups are those found to be inaccessible during a cross-check. No attempt is made to delete the files containing the backup from disk or tape; this action only updates the RMAN repository.
To delete expired backups:
On the Database Home page, click Availability to display the Availability subpage.
In the Backup/Recovery section, click Manage Current Backups.
The Manage Current Backups page appears.
In the Manage Current Backups page, click Delete All Expired.
This action deletes expired backup sets and expired image copies from the RMAN repository, regardless of which subpage is currently active.
The Delete All Expired: Specify Job Parameters page appears.
Optionally, select Perform the operation 'Crosscheck All' before 'Delete All Expired'.
By performing the cross-check immediately before deleting expired backups, RMAN will have up-to-date information about which backups are expired.
Click Submit Job.
A message should appear indicating that your job was successfully submitted.
If one or more specific backups are unavailable because of a temporary condition, such as a disk drive that is temporarily offline or a tape stored offsite, then you can mark those backups as unavailable. RMAN does not use unavailable backups to restore or recover data.
Note:
Backups stored in the flash recovery area cannot be marked as unavailable.RMAN keeps the record of unavailable backups in the RMAN repository and does not delete backups listed as unavailable when you delete expired backups. If the unavailable backups become accessible again, then you can mark them as available.
To mark backups as available or unavailable:
On the Database Home page, click Availability to display the Availability subpage.
In the Backup/Recovery section, click Manage Current Backups.
The Manage Current Backups page appears.
In the Search section, find the backups whose status you want to change.
Click the Select check box next to each backup in the Results list of backups.
Do one of the following:
Select Change to Available.
Select Change to Unavailable.
Note:
If you restricted the backups listed by searching only for available backups, only the Change to Unavailable button appears. If you restricted the backups listed by searching only for unavailable backups, only the Change to Available button appears.A confirmation message appears.
Click Yes to perform the change operation.
This section explains how to delete obsolete backups, which are those no longer needed by the configured retention policy. If you use a flash recovery area as your only disk-based backup destination, then you never need to delete obsolete backups from disk. The flash recovery area will keep files as specified by the retention policy, and delete them only when space is needed.
To delete obsolete backups:
On the Database Home page, click Availability to display the Availability subpage.
In the Backup/Recovery section, click Manage Current Backups.
The Manage Current Backups page appears.
Click Delete All Obsolete.
All obsolete backups (both backup sets and image copies) will be deleted, regardless of whether you clicked Delete All Obsolete while viewing the Backup Sets or Image Copies subpage.
The Delete All Obsolete: Specify Job Parameters page appears.
In the Schedule section, do one of the following:
Select One Time (Immediately) to run the deletion job immediately.
Schedule the deletion as you would a backup job.
Click Submit Job.