| Oracle® Database 2 Day + Performance Tuning Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B28275-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database 2 Day + Performance Tuning Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B28275-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Performance degradation of the database over time happens when your database was performing optimally in the past, such as 6 months ago, but has gradually degraded to a point where it becomes noticeable to the users. The Automatic Workload Repository (AWR) Compare Periods report enables you to compare database performance between two periods of time.
While an AWR report shows AWR data between two snapshots (or two points in time), the AWR Compare Periods report shows the difference between two periods (or two AWR reports, which equates to four snapshots). Using the AWR Compare Periods report helps you to identify detailed performance attributes and configuration settings that differ between two time periods. The two time periods selected for the AWR Compare Periods report can be of different durations. The report normalizes the statistics by the amount of time spent on the database for each time period and presents statistical data ordered by the largest difference between the periods.
For example, a batch workload that historically completed in the maintenance window between 10:00 p.m. and midnight is currently showing poor performance and completing at 2 a.m. You can generate an AWR Compare Periods report from 10:00 p.m. to midnight on a day when performance was good and from 10:00 a.m. to 2 a.m. on a day when performance was poor. The comparison of these reports should identify configuration settings, workload profile, and statistics that were different in these two time periods. Based on the differences identified, you can more easily diagnose the cause of the performance degradation.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Baselines are an effective way to diagnose performance problems. AWR supports the capture of baseline data by enabling you to specify and preserve a pair or a range of snapshots as a baseline. The snapshots contained in a baseline are excluded from the automatic AWR purging process and are retained indefinitely.
A moving window baseline corresponds to all AWR data that exists within the AWR retention period. Oracle Database automatically maintains a system-defined moving window baseline. The default size of the window is the current AWR retention period, which by default is 8 days.
This section contains the following topics:
Before creating a baseline, carefully consider the time period you choose as a baseline because it should represent the database operating at an optimal level. In the future, you can compare these baselines with other baselines or snapshots captured during periods of poor performance to analyze performance degradation over time.
You can create the following types of baseline:
A single baseline is captured at a single, fixed time interval. For example, a single baseline may be captured on March 5, 2007 from 5:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m.
You can choose a start time and an end time that are in the future to create a baseline that captures future database activity. If both the start time and the end time are in the future, a baseline template with the same name as the baseline will also be created. A baseline template is a specification that enables Oracle Database to automatically generate a baseline for a future time period.
To create a single baseline:
From the Database Home page, click Server.
The Server subpage appears.
Under Statistics Management, click AWR Baselines.
The AWR Baselines page appears with a list of existing baselines displayed.
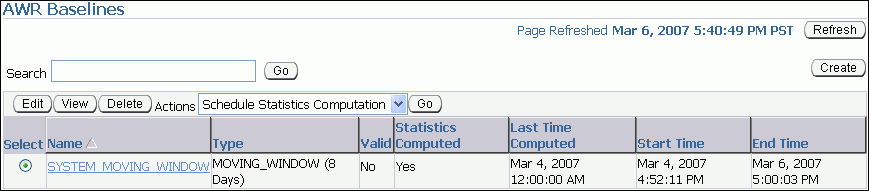
Click Create.
The Create Baseline: Baseline Interval Type page appears.
Select Single.

Click Continue.
The Create Baseline: Single Baseline page appears.
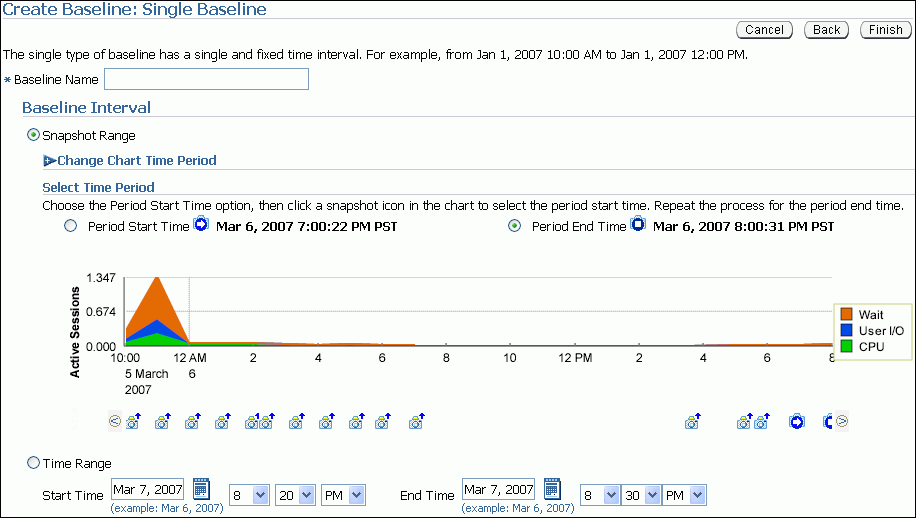
In the Baseline Name field, enter a name for the baseline.
Under Baseline Interval, select whether to use a snapshot range or a time range for the baseline. Do one of the following:
To use a snapshot range, select Snapshot Range. Complete the following steps:
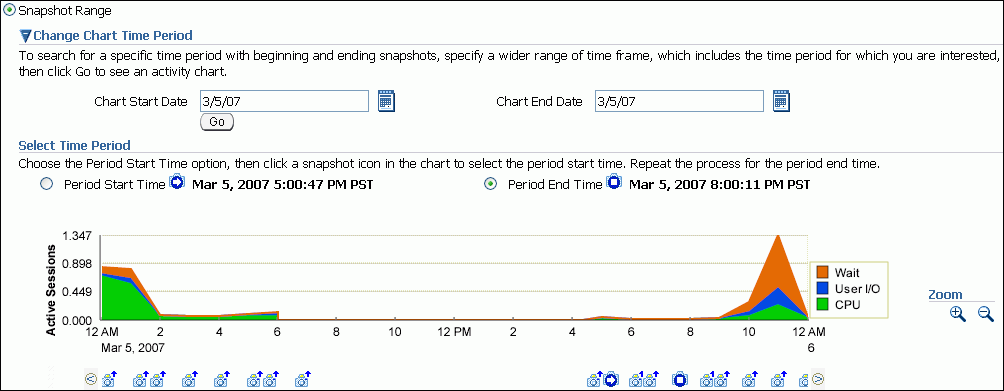
Optionally, to view older snapshots that are not displayed below the Active Sessions chart, expand Change Chart Time Period. Enter the desired start date in the Chart Start Date field and the desired end date in the Chart End Date field, and click Go.
Under Select Time Period, select a start time for the baseline by selecting Period Start Time and the snapshot icon below the Active Sessions chart that corresponds to the desired start time.
Select an end time for the baseline by selecting Period End Time and the snapshot icon below the Active Sessions chart that corresponds to the desired end time.
In this example, a snapshot range on March 5, 2007 from 5:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. is selected.
To use a time range, select Time Range. Complete the following steps:
In the Start Time fields, select a start time for the baseline.
In the End Time fields, select an end time for the baseline.
In this example, a time range from 5:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. on March 5, 2007 is selected.

Click Finish.
The AWR Baselines page reappears with the newly created baseline displayed.
A repeating baseline is a baseline that repeats during a time interval over a specific period. For example, a repeating baseline may repeat every Monday from 5:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. for the year 2007.
To create a repeating baseline:
From the Database Home page, click Server.
The Server subpage appears.
Under Statistics Management, click AWR Baselines.
The AWR Baselines page appears with a list of existing baselines displayed.
Click Create.
The Create Baseline: Baseline Interval Type page appears.

Select Repeating and then click Continue.
The Create Baseline: Repeating Baseline Template page appears.
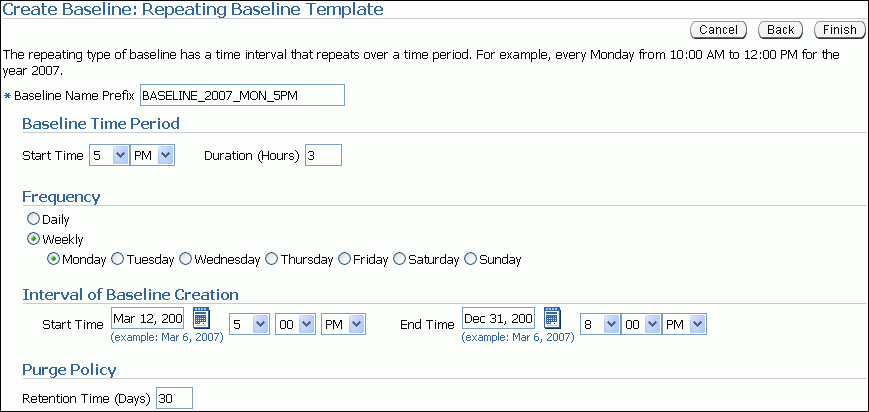
In the Baseline Name Prefix field, enter a name prefix for the baseline.
Under Baseline Time Period, specify the time of the day that you want the baseline to begin collecting AWR data and the duration of the baseline collection.
Under Frequency, do one of the following:
Select Daily if you want the baseline to repeat on a daily basis.
Select Weekly if you want the baseline to repeat on a weekly basis and select the day of the week on which the baseline will repeat.
Under Interval of Baseline Creation, complete the following steps:
In the Start Time fields, select a date and time in the future when the data collection should begin.
In the End Time fields, select a date and time in the future when the data collection should end.
Under Purge Policy, enter the number of days to retain baselines that have been captured.
Click Finish.
A baseline template with the same name as the baseline name prefix will also be created. A baseline template is a specification that enables Oracle Database to automatically generate a baseline for a future time period.
In this example, a repeating baseline that repeats weekly on Mondays from 5:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. for the year 2007 will be created.
To conserve storage space, you may want to periodically delete unused baselines stored in the database.
To delete a baseline:
From the Database Home page, click Server.
The Server subpage appears.
Under Statistics Management, click AWR Baselines.
The AWR Baselines page appears with a list of existing baselines displayed.
Select a baseline and click Delete.
The Confirmation page appears.
Select whether to purge the underlying data associated with the baseline.
The underlying data includes the individual snapshots preserved in the baseline and any statistics that are computed for the baseline. Do one of the following:
To delete the underlying data, select Purge the underlying data associated with the baseline.
To preserve the underlying data, select Do not purge the underlying data associated with the baseline.
Click Yes.
The AWR Baselines page reappears. A message informs you that the baseline was deleted successfully.
Computing threshold statistics for baselines enables you to graphically display the computed statistics in the charts on the Performance page.
To compute threshold statistics for baselines:
From the Database Home page, click Server.
The Server subpage appears.
Under Statistics Management, click AWR Baselines.
The AWR Baselines page appears with a list of existing baselines displayed.
Select the baseline for which you want to compute statistics.
Select a baseline that does not already have computed statistics. These baselines are identified by No in the Statistics Computed column.
From the Actions list, select Schedule Statistics Computation, and then click Go.
The Compute Threshold Statistics page appears.
In the Name field, enter a name for the task.
Alternatively, you can choose to use the system-generated name.
In the Description field, enter a description for the task.
Alternatively, you can choose to use the system-generated description.
Under Start, do one of the following:
Select Immediately to run the task immediately after it has been submitted.
Select Later to run the task at a later time as specified using the Date and Time fields.
Click Submit.
The AWR Baselines page appears. A message informs you that statistics computation has been scheduled for the selected baseline.
See Also:
"Customizing the Database Performance Page" for information about displaying computed statistics on the Performance page
Oracle Database 2 Day DBA for information about thresholds and how to manage them
As explained in "Setting Metric Thresholds for Performance Alerts", a metric is the rate of change in a cumulative statistic. Alerts notify you when particular metric thresholds are crossed. When the metric thresholds are crossed, the system is in an undesirable state. You can edit the threshold settings for baseline metrics.
You can create the following types of baseline:
This section describes the easiest technique for setting the metric thresholds for the default moving baseline. You can choose a group of basic metric threshold settings based on common database workload profiles: OLTP, data warehousing, and OLTP with nighttime batch jobs. After choosing a workload profile, you can expand or change the threshold values as needed.
To set metric thresholds for the default moving baseline:
On the Database Home page, under Related Links, click Baseline Metric Thresholds.
The Threshold Configuration tab of the Baseline Metric Thresholds page appears.
Click Quick Configuration.
The Quick Configuration: Baseline Metric Thresholds page appears.
In Workload Profile, select one of the following options, depending on how you are using the database:
Primarily OLTP (pure transaction processing 24 hours a day)
Primarily Data Warehousing (query and load intensive)
Alternating (OLTP during the daytime and batch during the nighttime)
In this example, select Primarily OLTP.
Click Continue.
The Quick Configuration: Review OLTP Threshold Settings page appears.
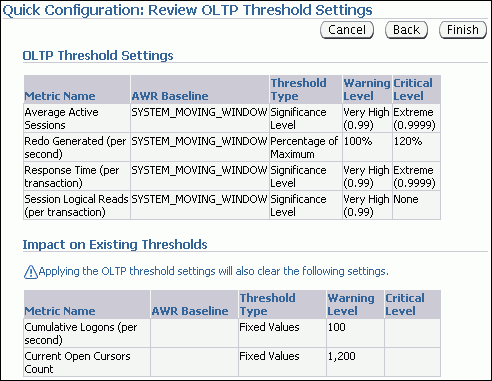
Review the metric threshold settings and click Finish.
You are returned to the Baseline Metric Thresholds page, with the Threshold Configuration tab selected. The metric threshold settings are displayed.
This section explains how to select a baseline and edit its thresholds. You can configure the type of threshold, for example, whether it is based on significance levels, percentage of maximum values, or fixed values. You can also configure the threshold levels that determine when the system generates critical alerts and warnings.
You can edit thresholds for the default moving baseline or a baseline that you created in the AWR Baselines page. You can select a baseline in the Edit Thresholds page after you have scheduled statistics computation from the AWR Baselines page and the statistics have finished computing on the static baseline.
To set a metric threshold for the default moving baseline:
On the Database Home page, under Related Links, click Baseline Metric Thresholds.
The Threshold Configuration tab of the Baseline Metric Thresholds page appears.
In the View list, select Basic Metrics.
The Baseline Metric Thresholds page appears.
In the Category/Name column, click the link for the metric whose threshold you want to set or change. For example, click Number of Transactions (per second).
The Edit Thresholds: Number of Transactions (per second) appears.
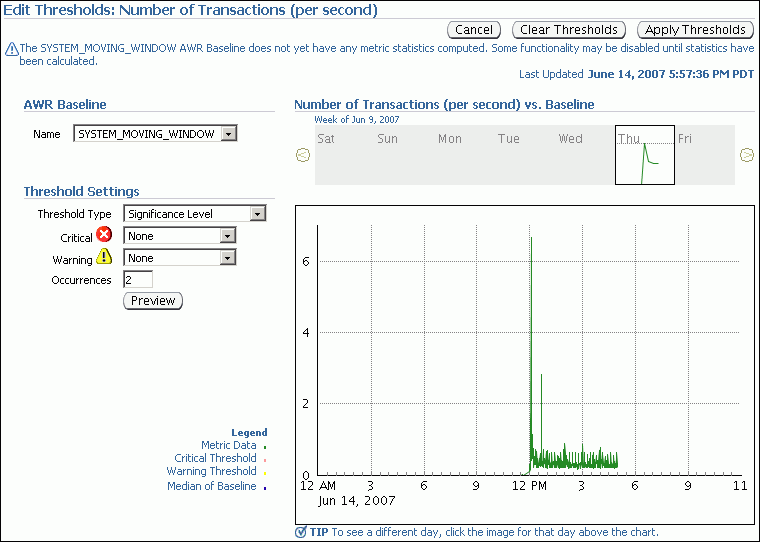
The charts on this page provide thumbnail and detailed views of metric activity for a 24-hour period. In the top thumbnail chart, click a day to view the value of the metric plotted against a 24-hour period.
Under AWR Baseline, in the Name list, select either the default SYSTEM_MOVING_WINDOW or the name of a baseline created in the AWR Baselines page.
A baseline appears in the AWR Baseline list after you have scheduled statistics computation from the AWR Baselines page and the statistics have finished computing on the static baseline.
In this example, select AWR_BASELINES_2007.
The page refreshes to show the charts for the baseline that you selected.
In the Threshold Settings section, complete the following steps:
In Threshold Type, leave Significance Level selected.
In Critical, select Extreme.
In Warning, select Very High.
In Occurrences, leave the current value.
Click Apply Thresholds.
You are returned to the Baseline Metric Thresholds page. This page shows the altered metric threshold settings.
This section describes how to run the Automatic Workload Repository (AWR) Compare Periods reports using Oracle Enterprise Manager.
You can use AWR Compare Periods reports to compare the database performance between two time periods by:
When performance degradation happens to a database over time, you should run the AWR Compare Periods report to compare the degraded performance, captured as a new baseline or a pair of snapshots, to an existing baseline. You will need a baseline that represents the system operating at an optimal level. If an existing baseline is not available, then you can compare database performance between two periods of time by using two arbitrary pairs of snapshots, as described in "Comparing Two Pairs of Snapshots".
To compare a baseline to another baseline:
From the Database Home page, click Server.
The Server subpage appears.
Under Statistics Management, click Automatic Workload Repository.
The Automatic Workload Repository page appears.
Under Manage Snapshots and Baselines, click the link next to Baselines.
The AWR Baselines page appears.
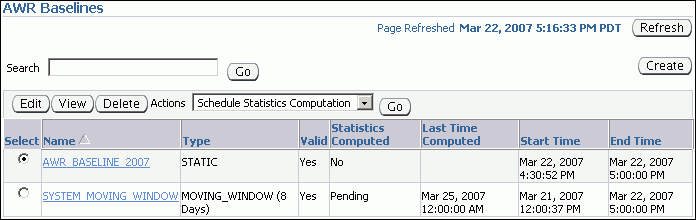
Complete the following steps:
Select the baseline to use for the report.
At least one existing baseline must be available.
From the Actions list, select Compare Periods and click Go.
The Compare Periods: Second Period Start page appears. Under First Period, the selected baseline is displayed.
In this example, the baseline named AWR_BASELINE_2007 is selected.

Compare the baseline selected in the first period to another baseline or a pair of snapshots. Do one of the following:
To compare to another baseline, select Select a Baseline and the baseline you want to use in the second period, and then click Next.
In this example, the baseline named SYSTEM_MOVING_WINDOW is selected.
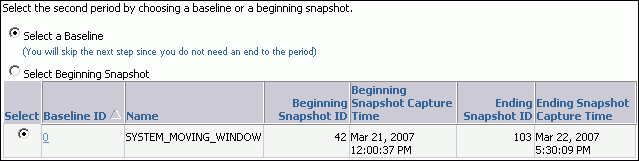
The Compare Periods: Review page appears. Go to Step 7.
To compare to a pair of snapshots, select Select Beginning Snapshot and the beginning snapshot to use in the second period, and then click Next.
In this example, snapshot 102, taken on March 22, 2007 at 5:00 p.m., is selected.
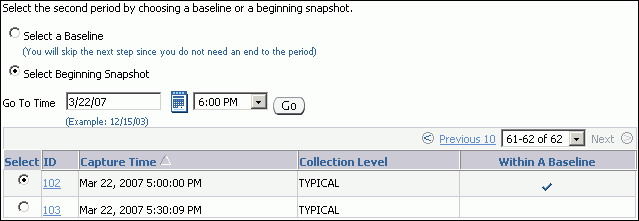
The Compare Periods: Second Period End appears. Proceed to the next step.
Select the ending snapshot for the snapshot period that will be included in the report and click Next.
In this example, snapshot 103, taken on March 22, 2007 at 5:30 p.m., is selected.
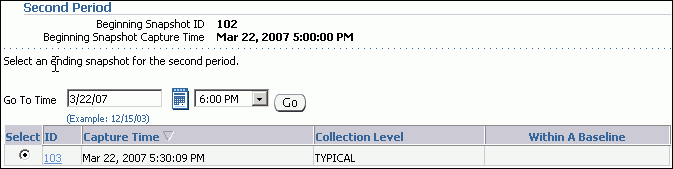
The Compare Periods: Review page appears.
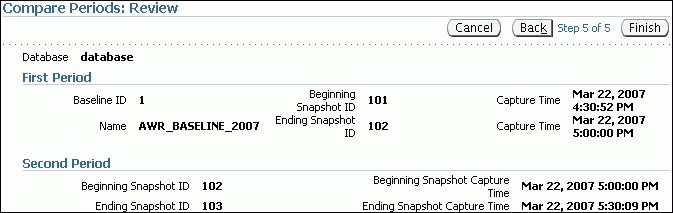
Review the periods to be included in the report and click Finish.
The Compare Periods: Results page appears.
Data from the selected periods appears under the General subpage. You can view data per second or per transaction by selecting an option from the View Data list.
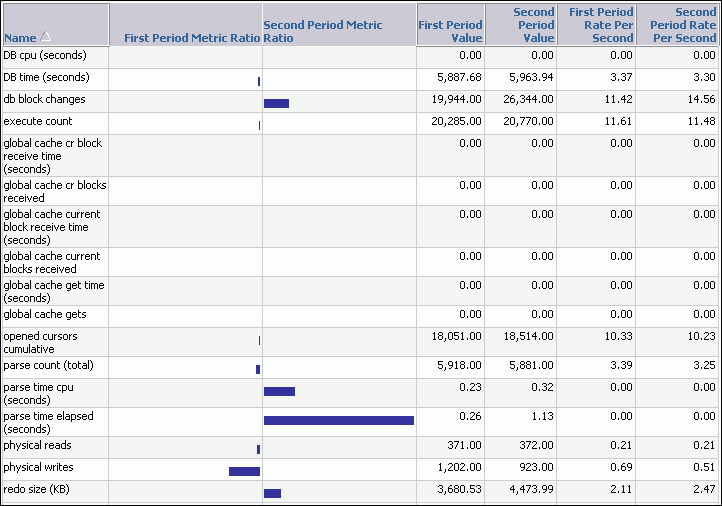
In this example, parse time in the second period is much higher than the first.
Click Report to view the report.
The Processing: View Report page appears while the report is being generated. After it completes, the report will appear. To change periods, click Change Periods. To save the report as an HTML file, click Save to File.
If an existing baseline is not available, then you can compare the database performance by using two arbitrary pairs of snapshots, one pair taken when the database is performing optimally, and another pair when the database is performing poorly. At least four existing snapshots must be available.
To compare performance using two pairs of snapshots:
From the Database Home page, click Server.
The Server subpage appears.
Under Statistics Management, click Automatic Workload Repository.
The Automatic Workload Repository page appears.

Under Manage Snapshots and Baselines, click the link next to Snapshots.
The Snapshots page appears.
From the Go To Time list, select the time for the starting snapshot and click Go.
This action filters the snapshots and displays only the snapshot taken at the start of the comparison period. The time in this example is 5:00 p.m. on March 21, 2007.
Under Select Beginning Snapshot, select the starting point for the first snapshot period to be included in the report.
In this example, snapshot 53, taken on Mar 21, 2007 5:00 p.m., is selected.
From the Actions list, select Compare Periods and click Go.
The Compare Periods: First Period End page appears.
Select the ending point for the first snapshot period to be included in the report and click Next.
In this example, snapshot 55, taken on Mar 21, 2007 6:00 p.m., is selected.
The Compare Periods: Second Period Start page appears.
Select the starting point for the second snapshot period to be included in the report and click Next.
In this example, snapshot 104, taken on March 22, 2007 at 6:00 p.m., is selected.
The Compare Periods: Second Period End page appears.
Select the end point for the second period that will be included in the report and click Next.
In this example, snapshot 106, taken on March 22, 2007 at 7:00 p.m., is selected.
The Compare Periods: Review page appears.

Review the selected periods that will be included in the report and click Finish.
The Compare Periods: Results page appears.
Data from the selected periods appears under the General subpage. You can view data per second or per transaction by selecting an option from the View Data list.
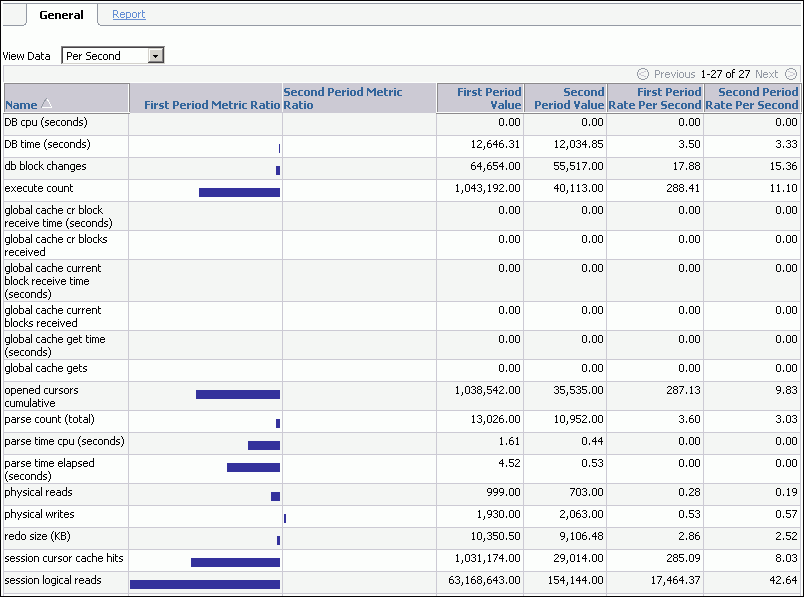
In this example, the first period shows significantly more activity, especially in session reads, than the second period.
To view the report, click the Report tab.
The Processing: View Report page appears while the report is being generated. After it completes, the report will appear. To change periods, click Change Periods. To save the report as an HTML file, click Save to File.
After an AWR Compare Periods report is generated for the time periods you want to compare, you can use it to perform an analysis of performance degradation with Oracle Database that may have happened over time. To learn how to generate AWR Compare Periods reports, see "Running the AWR Compare Periods Reports".
Figure 8-1 shows an example of an AWR Compare Periods report.
The AWR Compare Periods report is divided into the following sections:
The report summary is at the beginning of the AWR Compare Periods report, and summarizes information about the snapshot sets and loads used in the report. The report summary contains the following sections:
The Snapshot Sets section displays information about the snapshot sets used for this report, such as instance, host, and snapshot information.
In the example shown in Figure 8-1, the first snapshot period corresponds to the time when performance was stable on March 21, 2007 from 1:59 p.m. to 4:00 p.m. The second snapshot period corresponds to the time when performance degradation occurred on March 22, 2007 from 9:00 p.m. to 11:00 p.m.
The Host Configuration Comparison section compares the host configurations used in the two snapshot sets. For example, the report compares physical memory and number of CPUs. Any differences in the configurations are quantified as percentages in the %Diff column.
The System Configuration Comparison section compares the database configurations used in the two snapshot sets. For example, the report compares the SGA and log buffer size. Any differences in the configurations are quantified as percentages in the %Diff column.
The Load Profile section compares the loads used in the two snapshot sets. Any differences in the loads are quantified as percentages in the %Diff column.
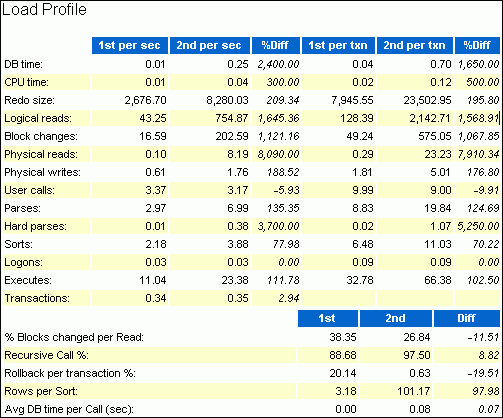
The Top 5 Timed Events section displays the five timed events or operations that consumed the highest percentage of total DB time in each of the snapshot sets.
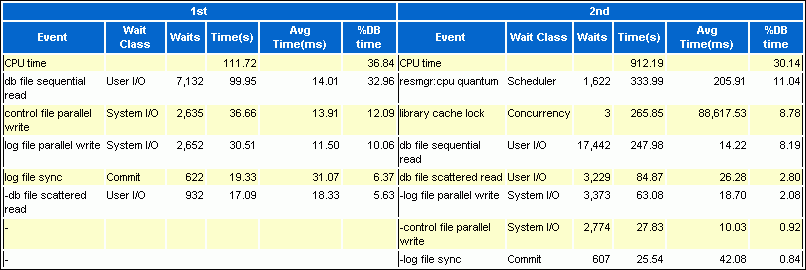
In this example, CPU time is over eight times higher in the second period than in the first. The number of waits for the db file sequential read event in the second period is over double the number in the first.
The details section follows the summary of the AWR Compare Periods report, and provides statistics about the snapshot sets and loads used in the report. For example, the section includes statistics for database time, wait events, SQL execution time, and instance activity.
The supplemental information is at the end of the AWR Compare Periods report, and provides additional information about initialization parameters and SQL statements. The init.ora Parameters section lists all the initialization parameter values for the first snapshot set. The Complete List of SQL Text section lists each statement by SQL ID and shows the text of the SQL statement.