|
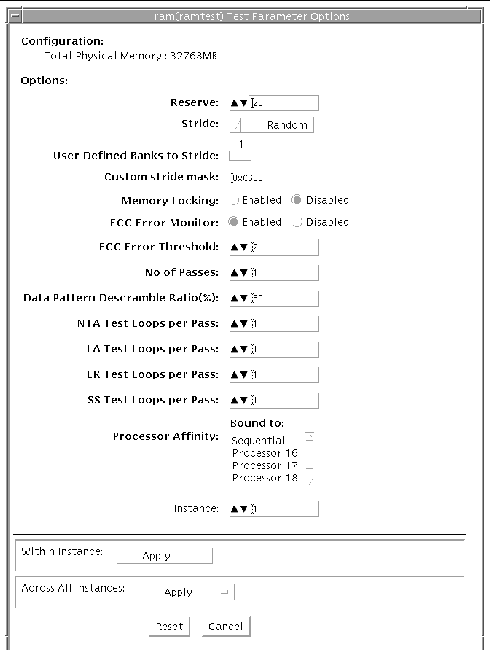
reserve
|
This is used to specify the amount of memory that will not be allocated for testing. Reserve represents a percentage of the total physical memory in the system. When the test starts, it probes the total memory present in the system, then tries to allocate (100 - reserve)% of memory. If the allocation or locking does not succeed the amount of memory is reduced before the retry. Before starting the test, the amount of memory allocated for testing is displayed.
Default value for reserve option is 20. For US IIIi platforms, default value is tuned to 25.
It should be noted that on low memory systems, the reserve value should be kept higher to avoid excessive swapping.
For 32-bit booted systems, the reserve value represents the percentage of 4 GB rather than the percentage of total physical memory.
|
|
stride
|
By default stride is set to "Random". It can be set to "Column" or "Row" also. In case of random, either Row or Column are randomly selected for each pass. Value of stride defines the memory locations addressed consecutively in certain subtests, in a hardware dependent manner. All testable memory is still tested. Using different stride checks coupling among a different set of memory cells, therefore random is the recommended value for this option unless both column and row are being explicitly used in different instances. For FA type of uses, stride may also be set to "UserDefined", in this case the test will stride the number of banks specified in the "userstride" option.
Stride may be set to "Custom" in which case the stride values are randomly selected from the strides specified in the "stridemask" value.
|
|
userstride
|
Use this option to set number of banks the test should stride. One of the good choices could be the interleave on the suspect bank, during FA. the value is limited between 1 and 16 right now. (This also means row striding is not possible while using this option).
|
|
stridemask
|
When stride=custom is selected, this value specifies the strides used. Each thread selects one of the stride values from stridemask by selecting one of the bits in the mask.The bits in the stridemask value represent the Least Significant Bit of the stride. Thus a value of 0x4000 calls for a stride of 16384 (using Bit 14 of the address). Mulitple bits can be set mixing row and column strides. Consult the Memory Controller section of the PRM for the CPU of the test system to discover how the memory reference address is divided between rows and columns in the DRAM.The value can be specified as a Decimal (NNN), Hexadecimal (0xNNN), or Octal (0NNN) value. The maximum value is 0x400000 (4194304). The default value is 0xC600 which represents strides using Bits 15, 14, 10, and 9.
|
|
lock
|
By default memory locking is "Disabled". To turn it on set lock to "Enabled". The test uses ISM to lock the memory into the core, this gives 4 MB virtual pages and avoids swapping. Running without locking on the other hand, adds more randomness to the addressing sequence.It should be noted that on low memory systems, this option can be "Enabled" to avoid excessive swapping.In case the test is unable to lock the memory, the user should put the following lines in /etc/system and reboot the machine.set shmsys:shminfo_shmmax=0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
set shmsys:shminfo_shmmin=1set shmsys:shminfo_shmmni=100set shmsys:shminfo_shmseg=10
|
|
eccmonitor
|
ECC Monitor is "Enabled" by default. The ECC error monitor runs as a separate thread in the test. When an ECC error is detected, the message is displayed on to the test output. The monitor can be turned off by setting this option to "Disabled".
|
|
threshold
|
This is the number of ECC errors after which the test will stop (if ECC monitor is running). When the threshold is reached the test will exit with a non zero exit code. If set to zero, the test will still report all the errors but will not stop. The default threshold is 2.
|
|
pass
|
This option specifies number of passes, in the same instance. Increasing pass is recommended in case "lock" is enabled, this will save time spent on locking the memory every time a new process/instance is spawned by the VTS kernel. Note that this pass has no relation with the system passes in the VTS infrastructure, it will appear that ramtest is taking longer to complete system passes.
|
|
ntaloops
|
Specifies number of loops of NTA march(30N) test, per pass. Increasing the number of loops of any subtest increases the relative time spent on that subtest in each pass. This increase also increases the time taken to complete a pass. NTA march test attacks stuck-at-faults, two cell coupling faults, and some three cell coupling faults.
|
|
laloops
|
Specifies number of loops of LA march(22N) test, per pass. Increasing the number of loops of any subtest increases the relative time spent on that subtest in each pass. This increase also increases the time taken to complete a pass. LA march test attacks coupling and stuck-at-faults.
|
|
ntaloops
|
Specifies number of loops of NTA march test, per pass. Increasing the number of loops of any subtest increases the relative time spent on that subtest in each pass. This increase also increases the time taken to complete a pass. NTA march test attacks coupling and stuck at faults.
|
|
lrloops
|
Specifies number of loops of LR march(14N) test, per pass. Increasing the number of loops of any subtest increases the relative time spent on that subtest in each pass. This increase also increases the time taken to complete a pass. LR march test attacks coupling and stuck-at-faults.
|
|
dratio
|
Descramble ratio can be used to tune the algorithm used to generate data patterns in ramtest. Descramble ratio of 100 means that all the data patterns generated will be descrambled. Where as if descramble ratio is 0, the test will generate the data patterns tuned towards bus noise. Default value is 50, which means that half the data patterns are descrambled.
|
|
ssloops
|
Specifies number of loops of SS march(22N) test, per pass. Increasing the number of loops of any subtest increases the relative time spent on that subtest in each pass. This increase also increases the time taken to complete a pass. SS march test attacks simple static faults.
|
|
custom
|
When stride=custom is selected, this value specifies the strides used. Each thread selects one of the stride values from stridemask by selecting one of the bits in the mask.The bits in the stridemask value represent the Least Significant Bit of the stride. Thus a value of 0x4000 calls for a stride of 16384 (using Bit 14 of the address). Mulitple bits can be set mixing row and column strides. Consult the Memory Controller section of the PRM for the CPU of the test system to discover how the memory reference address is divided between rows and columns in the DRAM.The value can be specified as a Decimal (NNN), Hexadecimal (0xNNN), or Octal (0NNN) value. The maximum value is 0x400000 (4194304). The default value is 0xC600 which represents strides using Bits 15, 14, 10, and 9.
|