Fast Frame Buffer Test (ffbtest)
|
ffbtest verifies the functionality of the fast frame buffer (FFB).
ffbtest can detect and adapt to the video modes of single- and double-buffer versions of the FFB. All ffbtest tests can run in several screen resolutions such as standard, stereo, and high resolution. In stereo mode, all tests write into the right and left eyes unless you specify otherwise. This test also supports FFB, FFB2, and FFB2+ fast frame buffer configurations. Use the ffbconfig -prconf command to display the configuration of the frame buffer you want to test.
You can interrupt ffbtest using Control-C.
Test accuracy is checked using a checksum algorithm. Possible locations of failing pixels are identified, as well as the likely failing FRU.
|
Caution - Do not run any other application or screen saver program that uses the FFB accelerator port while running ffbtest. These programs cause SunVTS to return incorrect errors. To ensure you are not running any wrong programs perform the following procedures.
|
Turn off the screen saver:
# /usr/openwin/bin/xset s off
|
Turn off the Energy Power features:
# /usr/openwin/bin/xset -dpms
|
Turn off the Frame Buffer Power features:
# /usr/openwin/bin/xset -fbpm
|
Edit the autopm parameter in the /etc/power.conf file as follows:
# Copyright (c) 1996 - 1999 by Sun Microsystems, Inc.# All rights reserved.##pragma ident "@(#)power.conf 1.14 99/10/20 SMI"## Power Management Configuration File## NOTE: The entry below is only used when no windowing environment# is running. When running windowing environment, monitor power# management is controlled by the window system.device-dependency /dev/fb /dev/kbddevice-thresholds /dev/kbd always-on# Auto-Shutdown Idle(min) Start/Finish(hh:mm) Behaviorautoshutdown 30 9:00 9:00 unconfiguredautopm disable
|
ffbtest Test Requirements
Disable all screen savers before testing any graphics device. Type xset s off at a UNIX prompt to disable the Solaris screen saver. Disable the Power Management software if it is running.
software if it is running.
For full instructions on testing frame buffers, see The SunVTS 5.1 Test Reference Manual.
ffbtest requires approximately 7 MB of disk space in the /tmp directory to extract its working files. If this space is not available, the diagnostic will fail and report warning and error messages, indicating a lack of disk space.
To start SunVTS with vtsui, but without vtsk, you must add the host name to xhost as: xhost + <hostname>.
ffbtest Options
To reach the dialog box below, right-click on the test name in the System Map and select Test Parameter Options. If you do not see this test in the System Map, you might need to expand the collapsed groups, or your system may not include the device appropriate to this test. Refer to the SunVTS User's Guide for more details.
FIGURE 12-1 ffbtest Test Parameter Options Dialog Box
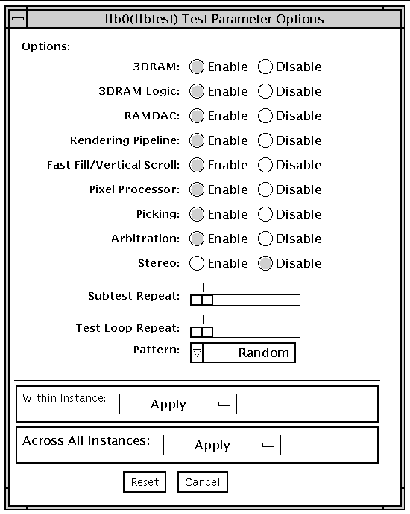
By default, all tests are enabled except the stereo test.
TABLE 12-1 ffbtest Options
|
ffbtest Options
|
Description
|
|
3DRAM test
|
The 3DRAM test thoroughly tests the video memory in the FFB using 512-bit reads and writes. 3DRAM makes a full screen pass, consisting of a write and a read to each pixel location, for each access mode on the list below. You can use either random data or specify data at the command line. A second pass is made with the one's complement of the data used in the first pass so that each memory location is tested with both a zero and a one. Notice that some passes are skipped on the single-buffered FFB.
Errors in this subtest are attributes to the 3DRAM. A failing chip is indicated by (X, Y) locations and device-specific "U" numbers:
-
DFB8R, DFB8G, DFB8B, DFB8X--Buffer A
-
DFB24--Buffer A
-
DFB32--Buffer A
-
SFB8R, SFB8G, SFB8B, SFB8X--Buffer A
-
SFB8R, SFB8G, SFB8B, SFB8X--Buffer B (double buffer only)
-
SFB32--Buffer A
-
SFB32--Buffer B (double buffer only)
-
SFB32--Buffer C (double buffer only)
-
SFB64--Buffers A and C (double buffer only)
-
SFB64--Buffers B and C (double buffer only)
|
|
3DRAM Logic test
|
3DRAM Logic provides logical functionality to the FFB. The following services are tested:
-
Compare Controls--Match AB
-
Compare Controls--Magnitude AB
-
Compare Controls--Match C (double buffer only)
-
Compare Controls--Magnitude C (double buffer only)
-
Match Mask--AB
-
Magnitude Mask--AB
-
Match Mask--C (double buffer only)
-
Magnitude Mask--C (double buffer only)
-
Raster Operations--RGB
-
Raster Operations--X
-
Raster Operations--YZ (double buffer only)
-
Plane Mask--RGB
-
Plane Mask--X
-
Plane Mask--Y
-
Plane Mask--Z
-
Group Enable--R, G, B, X
-
Group Enable--Y, Z (double buffer only)
|
|
3DRAM Logic test
(Continued)
|
ffbtest tests each function separately with a series of SFB64 writes. A total of 16 writes are made for each different test case with Y coordinate values varying from 0 to 30 in increments of 2 pixels. This dotted column organization provides page thrashing and block flashing in all screen resolutions. For each operation, all possible combinations are tested. For example, ROP RGB new==old has three possible values: new < old, new == old, and new > old. ffbtest tests each of these cases.
Five passes of the functions are made. Each pass writes into a different FFB address space: SFB32-A, SFB32-B, SFB32-C, SFB64-AC, and SFB64-BC. Note that the passes that write into the SFB32 address spaces are writing two pixels at a time because the tests use SFB64 writes.
For FFB2+ boards, additional testing is performed on the new stencil and passin capabilities if the board is DBZ.
Care is taken to ensure that all 3DRAM chips are tested. Errors in this subtest are attributed to the 3DRAM.
|
|
RAMDAC Test
|
RAMDAC registers are tested using simple read/write patterns to determine if there are any bad bits. This includes all LUTs. ffbtest ensures that data is actually being read from the RAMDAC and not being supplied by the driver.
Next, the RAMDAC Signature Register captures the pixels going to the screen. This test determines that all of the different data paths within the RAMDAC are functioning properly.
The following modes are tested:
-
24-bit true color from A
-
24-bit true linear color from A
-
24-bit direct color from A
-
24-bit true color from B (double buffer only)
-
24-bit true linear color from B
-
24-bit direct color from B (double buffer only)
-
8-bit pseudo color (from each plane in RGB) from A
-
8-bit pseudo color (from each plane in RGB) from B (double buffer only)
-
8-bit non-linear grayscale (from each plane in RGB) from A
-
8-bit non-linear grayscale (from each plane in RGB) from B (double buffer only)
-
8-bit linear grayscale (from each plane in XRGB) from A
-
8-bit linear grayscale (from each plane in XRGB) from B (double buffer only)
-
8-bit overlay pseudo color (from buffer A, X plane)
|
|
RAMDAC test
(Continued)
|
This test displays a total of 11 different types of windows on the screen for the single-buffered configuration; 22 for double-buffered. A cursor is also displayed on the screen.
RAMDAC on FFB2+ board supports three modes (SEP8, SEP4, and Combined). This test detects the RAMDAC type and tests the original and additional features like increased number of CLUTs, increased WLUT size, additional overlay WLUT.
Errors in this test are attributed to the RAMDAC.
|
|
Rendering Pipeline test
|
Rendering Pipeline uses the rendering pipeline tests developed for the FFB stand-alone diagnostics.
Each primitive is tested thoroughly with the following sources and configurations:
Errors in this test are attributed to the FBC.
|
|
Fast Fill/Vertical Scroll test
|
The Fast Fill/Vertical Scroll primitives are separated from the Rendering Pipeline tests because of their dependence on screen type. There are three different tests, one for each screen type. Each test uses both block and page mode fistfuls.
Errors in this test are attributed to the FBC.
|
|
Pixel Process test
|
Pixel Processor, a subtest, exercises the following options selected by the FFB's Pixel Processor Control (PPC) register:
-
Auxiliary clipping (additive and subtractive)
-
Depth cueing
-
Alpha blend
-
Viewport clip (2D and 3D)
-
Area pattern (transparent and opaque)
Errors in this test are attributed to the FBC.
|
|
Picking test
|
The Picking test exercises the pick detect login of the 3DRAM. ffbtest defines a pick detect window and checks that writes to the window are picked, and writes outside the window are not picked. The test is repeated once for each 3DRAM.
Errors in this test are attributed to the 3DRAM.
|
|
Arbitration test
|
The Arbitration subtest continuously renders an object into the accelerator port while performing reads and writes through the direct port. For single-buffered configurations, a picture is rendered into the RGB planes while another process does DFB reads and writes in the X plane. For doubled buffered configuration, a picture is rendered into all 32 planes of the B buffer while the other does 32-bit DFB reads and writes in the A plane. This subtest simulates conditions in the real world, where rendering processes and windows operations run concurrently.
Errors in this test are attributed to the FBC.
|
|
Stereo Test
|
The Stereo test displays an object in stereo mode with different images for the right and left eye. The user can verify proper operation by looking at the screen with stereo glasses and following the displayed instructions. If the monitor type is not 1280x1024 at 76MHz, this test prints a warning message and does not run. To prevent this message from being displayed or written to the SunVTS information log, disable the stereo test in the test option menu. Only Sony P4 and N2 monitors support stereo resolutions.
This test temporarily switches the monitor into stereo mode, renders a stereo image, performs a signature analysis on the stereo image (using the RAMDAC signature capture register), and after displaying the image for five seconds, restores the monitor to its previous resolution.
Errors in this test are attributed to the RAMDAC.
Note -- If vertical lines are displayed on the console when running SunVTS, this could be caused by the ffbtest stereo test. There is a time-critical period in the FFB hardware when trying to change the screen resolution from standard to stereo and back to standard. When the system is heavily loaded or running all of the SunVTS tests, the FFB device driver may get interrupted while changing screen resolution. If this occurs, FB ASIC and RAMDAC get out of synchronization, resulting in an unusual display on the FFB screen. This problem could also cause a system hang condition. To avoid this type of display problem, disable the ffbtest stereo test when other SunVTS tests are enabled.
This test is disabled by default because it is only needed when a stereo monitor and stereo glasses are present.
|
ffbtest Test Modes
Due to the nature of graphic tests, reading from or writing to the frame buffer during graphic tests will disturb user operation. This test is only available in offline Functional test and Stress mode.
TABLE 12-2 ffbtest Supported Test Modes
|
Test Mode
|
Description
|
|
Functional
(Offline)
|
The ffbtest verifies both the single- (SFB) and double-buffered (DBZ) fast frame buffer boards.
|
|
Stress mode
|
Stress mode exercises the frame buffer as much as possible. The Random test generator, constructed as part of the verification effort, is used. Starting from a known seed, random primitives with random attributes are generated. The primitives are checked to ensure that they were rendered in the same way as on a known good system. The test is repeated ten times, with each random picture overlaying the previous one.
Stress mode is not available on FFB2+ boards.
|
ffbtest Command-Line Syntax
/opt/SUNWvts/bin/ffbtest standard_arguments -o dev=device_name, S=subtest_number,F=#_of_subtest_loops,B=#_of_test_loops,P=test_pattern
TABLE 12-3 ffbtest Command-Line Syntax
|
Argument
|
Description
|
|
dev=device_name
|
device_name is the relative path name of the device being tested with respect to /dev/fbs; The default is ffb0.
|
|
S=subtest_number
|
subtest_number is the test number of the subtest to be run. Select from the subtests below. You can run multiple subtests by adding the subtest numbers. For example, n=0x3 runs both test 1 and test 2; n=0x180 runs both test 0x080 and test 0x0100. Note that you do not need the leading zeros.
-
n=0x00001 3DRAM
-
n=0x00002 3DRAM Logic
-
n=0x00004 RAMDAC
-
n=0x00008 Rendering Pipeline
-
n=0x00010 FastFill/Vertical Scroll
-
n=0x00020 Pixel Processor
-
n=0x00040 Picking
-
n=0x00080 Arbitration
-
n=0x00100 Stereo
More than one test can be selected by ORing subtest numbers. For example: n = 0x00009 selects 3DRAM and Rendering Pipeline tests. A hex number must be preceded by 0x, decimal numbers are also acceptable.
|
|
F=#_of_subtest_loops
|
Specifies the number of times to repeat each subtest. The default is 1.
|
|
B=#_of_test_loops
|
Specifies the number of times to repeat a test loop before passing. The default is 1.
|
|
P=test_pattern
|
Specifies the test pattern number. The default is r, for random patterns. You may also choose 0 for 0x0000000, 3 for 0x3333333, 5 for 0x5555555, or 9 for 0x9999999.
|
|
Note - 64-bit tests are located in the sparcv9 subdirectory: /opt/SUNWvts/bin/sparcv9/testname. If a test is not present in this directory, then it may only be available as a 32-bit test. For more information refer to the SunVTS 5.1 Test Referenct Manual.
|
|
Note - Errors returned by ffbtest are nonspecific. It is not possible to determine which component caused a failure. In all error conditions, the field replaceable unit (FRU) is the entire FFB.
|
| SunVTS 5.1 Patch Set 6 Documentation Supplement
| 817-6318-10
|    
|
Copyright © 2004, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 software if it is running.
software if it is running.
