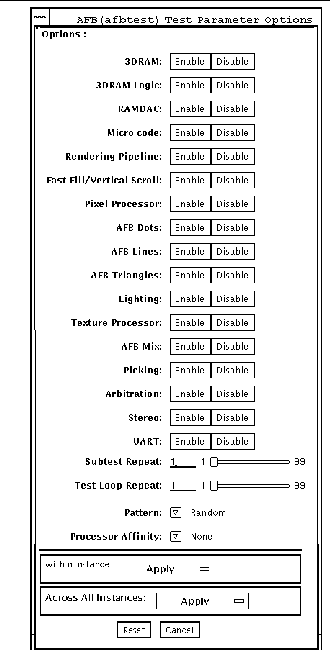
|
3DRAM test
|
The 3DRAM test thoroughly tests the video memory in the AFB using 512-bit reads and writes. 3DRAM makes a full-screen pass, consisting of a write and a read to each pixel location, for each access mode on the list below. The data used can be either random or specified by the user. A second pass is made with the one's complement of the data used in the first pass so that each memory location is tested with both a zero and a one.
Errors in this subtest are attributes to the 3DRAM. A failing chip is indicated by (X, Y) locations and device-specific "U" numbers.
-
DFB8R, DFB8G, DFB8B, DFB8X--Buffer A
-
DFB24--Buffer A
-
DFB32--Buffer A
-
SFB8R, SFB8G, SFB8B, SFB8X--Buffer A
-
SFB8R, SFB8G, SFB8B, SFB8X--Buffer B
-
SFB32--Buffer A
-
SFB32--Buffer B
-
SFB32--Buffer C
-
SFB64--Buffers A and C
-
SFB64--Buffers B and C
|
|
3DRAM Logic test
|
The 3DRAM Logic test provides logical functionality to the AFB. The following services are tested:
-
Compare Controls--Match AB
-
Compare Controls--Magnitude AB
-
Compare Controls--Match C
-
Compare Controls--Magnitude C
-
Match Mask--AB
-
Magnitude Mask--AB
-
Match Mask--C
-
Magnitude Mask--C
-
Raster Operations--RGB
-
Raster Operations--X
-
Raster Operations--YZ
-
Plane Mask--RGB
-
Plane Mask--X
-
Plane Mask--Y
-
Plane Mask--Z
-
Group Enable--R, G, B, X
-
Group Enable--Y, Z
Each function is tested separately with a series of SFB64 writes. A total of 16 writes are made for each different test case with Y coordinate values varying from 0 to 30 in increments of 2 pixels. This dotted column organization provides page thrashing and block flashing in all screen resolutions. For each operation all possible combinations are tested. For example, in ROP RGB new==old there are three possible values: new < old, new == old, and new > old. Each of these cases are tested.
Five passes of the functions are made. Each pass writes into a different AFB address space: SFB32-A, SFB32-B, SFB32-C, SFB64-AC, and SFB64-BC. Note that the passes that write into the SFB32 address spaces are writing two pixels at a time because the tests use SFB64 writes.
Care is taken to ensure that all 3DRAM chips are tested. Errors in this subtest are attributed to the 3DRAM.
|
|
RAMDAC test
|
RAMDAC registers are tested using simple read/write patterns to determine if there are any bad bits. This includes all LUTs (4 CLUTs, PWLUT and OWLUT). afbtest ensures that data is actually being read from the RAMDAC and not being supplied by the driver.
RAMDAC on AFB can be in SEP8 or Combined mode. RAMDAC test detects the RAMDAC mode and tests the RAMDAC output for that mode. The RAMDAC Signature Register captures the pixels going to the screen. This test determines that all of the different data paths within the RAMDAC are functioning properly.
The data pattern is designed so all the data paths are tested, that is, all CLUTs, PWLUTs, and OWLUTS. A cursor is also displayed on the screen.
Errors in this test are attributed to the RAMDAC.
|
|
Microcode test
|
Microcode test generates the checksum for the microcode of each enabled float and compares all the checksums for equality.
Errors in this test are attributed to the microcode PROMS & SRAMS.
|
|
Rendering Pipeline test
|
Rendering Pipeline test uses the rendering pipeline tests developed for the FFB stand-alone diagnostics. Each FFB primitive is tested thoroughly with a variety of sources and configurations:
Errors in this test are attributed to the Draw Chips.
|
|
Fast Fill/Vertical Scroll test
|
Fast Fill/Vertical Scroll primitives are separated from the Rendering Pipeline tests because of their dependence on screen type. There are three different tests, one for each screen type. Each test uses both block and page mode fast fills.
Errors in this test are attributed to the Draw Chips.
|
|
Pixel Process test
|
The Pixel Processor test, a subtest, exercises the options selected by the AFB's Pixel Processor Control (PPC) register:
-
Auxiliary clipping (additive and subtractive)
-
Depth cueing
-
Alpha blend
-
Viewport clip (2D and 3D)
-
Area pattern (transparent and opaque)
Errors in this test are attributed to the Draw Chips.
|
|
AFB Dots test
|
This test uses the AFB primitive tests developed for the AFB stand-alone diagnostics. AFB Dots are tested thoroughly with a variety of sources and configurations:
-
Dots
-
Anti-aliased dots
-
Big dots
Errors in this test are attributed to the Command & Draw Chips.
|
|
AFB Lines test
|
This test uses the AFB primitive tests developed for the AFB stand alone diagnostics. AFB Lines are tested thoroughly with a variety of sources and configurations:
Errors in this test are attributed to the Command & Draw Chips.
|
|
AFB Triangles test
|
This test uses the AFB primitive tests developed for the AFB stand alone diagnostics. AFB Triangles are tested thoroughly with a variety of sources and configurations:
-
Triangles drawn clockwise & counter clockwise
-
Triangles drawn as stripes
-
Independent triangles
-
Triangles drawn as stars
-
Triangles with facet normals
Errors in this test are attributed to the Command & Draw Chips.
|
|
Lighting test
|
The Lighting test exercises AFB float and lighting microcode. This test lights an object with maximum number of lights (32) that AFB can handle in hardware. A checksum is generated for the rendered image and compared with the checksum generated for the same image on a known good system.
Errors in this test are attributed to the Float & Microcode SRAMS.
|
|
Texture Processor test
|
The Texture Processor test exercises the different options of the AFB's Texture Pixel Processor Control (TPPC) register:
-
Texture Minification
-
Texture Magnification
-
Blend
-
Decal
-
Modulation
Errors in this test are attributed to the Draw Chips.
|
|
AFB Mix test
|
The AFB Mix test draws different primitives with variety combinations of sources and configurations, exercising all the Draw, Float, Microcode, and 3DRAM chips on AFB. This test is to stress the AFB.
Errors in this test are attributed to Draw, Float, Microcode, and/or 3DRAM Chips.
|
|
Picking test
|
The Picking test exercises the pick detect login of the 3DRAM. We define a pick detect window and make sure that writes to the window are picked, and writes outside the window are not picked. The test is repeated once for each 3DRAM.
Errors in this test are attributed to the 3DRAM.
|
|
Arbitration test
|
The Arbitration test, a subtest, continuously renders an object into the accelerator port while doing reads and writes through the direct port. A picture is rendered into all 32 planes of the B buffer while the other process does 32-bit DFB reads and writes in the A plane. This subtest simulates conditions in the real world, where rendering processes and windows operations run concurrently.
Errors in this test are attributed to the Context switching between DFB and SFB.
|
|
Stereo test
|
Stereo test displays an object in stereo mode with different images for the right and left eye. The user can verify proper operation by looking at the screen with stereo glasses and following the instructions being displayed. If the monitor type is not 1280x1024 at 76MHz, this test prints a warning message and does not execute.
To prevent this message from being displayed or written to the SunVTS information log, disable the stereo test in the Test Parameter Options dialog box. Only Sony P4 and N2 monitors support stereo resolutions. This test temporarily switches the monitor into stereo mode, renders a stereo image, performs a signature analysis on the stereo image (using the RAMDAC signature capture register), and after displaying the image for five seconds, restores the monitor to its previous resolution.
Errors in this test are attributed to the RAMDAC.
|
|
UART test
|
The UART test tests both UART0 and UART1. First, UART memory is tested using simple read/write patterns to determine if there are any bad bits. Then data is written to UART 0/1 and the written data is read using the internal loopback in polling mode. The read data is verified with written data.
Errors in this test are attributed to UART and its SRAM memory chip.
|